Introduction
For millions experiencing androgenetic alopecia, the search for effective hair loss treatment continues to evolve beyond traditional approaches. Topical finasteride has emerged as a promising alternative to oral medications, offering targeted treatment with potentially fewer systemic effects. However, researchers and clinicians are now exploring whether combining this medication with specific enhancers could unlock even better results for those struggling with pattern hair loss.
Recent scientific investigations have focused on three particularly promising enhancers: oestrogen, melatonin, and tretinoin. Each brings unique properties that may amplify the effectiveness of topical finasteride through different mechanisms. These combination treatments represent a sophisticated approach to addressing hair loss by targeting multiple pathways simultaneously, potentially offering hope to patients who haven’t achieved satisfactory results with single-agent therapy.
This comprehensive guide examines the science behind these innovative combinations, exploring how each enhancer works synergistically with topical finasteride to potentially improve treatment outcomes. We’ll delve into the mechanisms that make these combinations effective, compare their relative benefits and limitations, and address crucial safety considerations. Whether you’re considering treatment options or simply seeking to understand the latest advances in hair loss therapy, this evidence-based exploration provides essential insights into whether these enhanced formulations truly deliver superior results. From understanding basic principles to evaluating clinical evidence and practical considerations, we’ll equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your hair loss treatment journey.
Key Takeaways – TL/DR
- Topical finasteride combined with enhancers may improve hair regrowth compared to monotherapy
- Tretinoin enhances finasteride absorption and follicular penetration up to 3x
- Oestrogen combinations show promise for female pattern hair loss with minimal systemic effects
- Melatonin additions may accelerate hair growth cycles and reduce inflammation
- Safety profiles vary by combination, requiring personalized treatment approaches
Understanding Topical Finasteride for Hair Loss
Topical finasteride represents a significant advancement in treating androgenetic alopecia, offering targeted scalp treatment whilst minimising systemic exposure. This localised approach provides an alternative for patients seeking effective hair loss treatment without the concerns associated with oral medication, making it particularly appealing for those who have experienced side effects or prefer a more targeted therapeutic option.
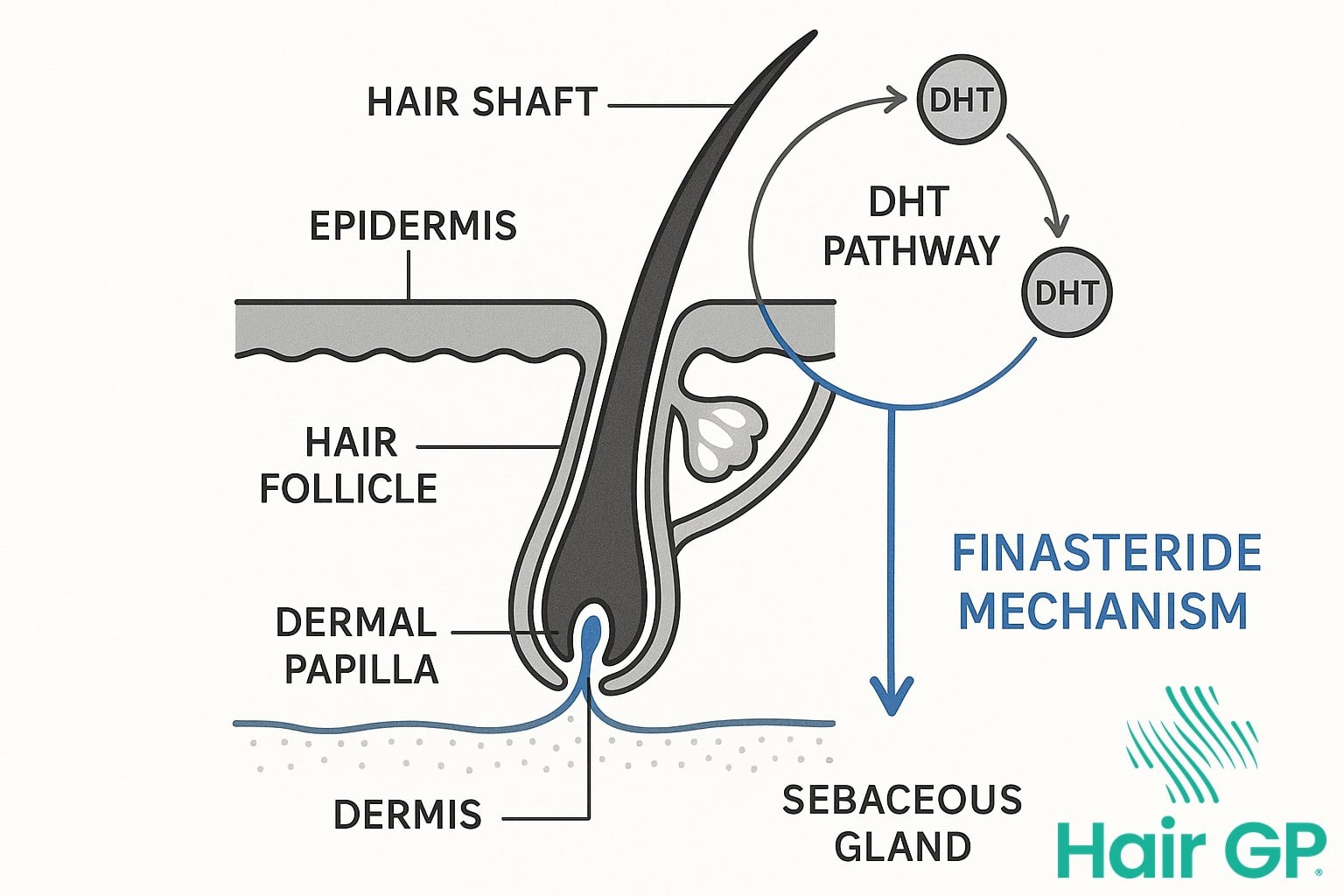
How Topical Finasteride Works
The mechanism of action for topical finasteride mirrors its oral counterpart, functioning as a selective inhibitor of type II 5-alpha reductase enzyme. This inhibition prevents the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) within the scalp tissue, addressing the primary hormonal driver of pattern hair loss. When applied directly to affected areas, the medication penetrates hair follicles and surrounding tissues, creating localised zones of DHT suppression.
Research demonstrates that topical formulations can reduce scalp DHT levels by approximately 68-75% [1], comparable to oral finasteride’s efficacy whilst maintaining significantly lower serum DHT suppression. This targeted approach helps prevent follicle miniaturisation, the progressive shrinking process that characterises androgenetic alopecia. By blocking DHT at the follicular level, topical finasteride allows weakened hair follicles to recover their normal growth cycles, potentially reversing miniaturisation and promoting thicker, healthier hair growth.
Topical vs Oral Finasteride
The primary distinction between topical and oral finasteride lies in their pharmacokinetic profiles and systemic exposure. Whilst oral finasteride typically reduces serum DHT by 60-70%, topical formulations achieve only 24-26% systemic reduction [2], suggesting superior localisation of therapeutic effects. This reduced systemic absorption translates to a lower incidence of reported side effects, particularly those affecting sexual function, which remain a concern for some oral finasteride users.
Clinical studies comparing both delivery methods have shown similar efficacy in treating androgenetic alopecia. A systematic review found that topical finasteride at concentrations of 0.25% demonstrated comparable hair count improvements to oral finasteride 1mg daily [2]. The topical route offers additional advantages including adjustable dosing, combination potential with other treatments, and the psychological benefit of direct application to affected areas.
However, topical application requires consistent technique and may present challenges such as scalp irritation or difficulty applying to areas with existing hair. Despite these considerations, the favourable safety profile and maintained efficacy make topical finasteride an increasingly popular choice for patients seeking effective hair loss treatment whilst minimising systemic medication exposure.
The Science Behind Combination Treatments
The rationale for combining topical finasteride with other therapeutic compounds stems from a fundamental understanding that hair loss involves multiple biological pathways. Researchers have discovered that whilst finasteride effectively blocks DHT production, combining it with complementary agents can address other aspects of hair follicle miniaturisation and potentially enhance treatment outcomes. This multi-targeted approach represents a significant advancement in combination therapy for androgenetic alopecia.
Synergistic Mechanisms
The concept of synergistic effects in hair growth treatments relies on targeting complementary pathways that contribute to follicular health. When topical finasteride is combined with other active compounds, the resulting therapeutic effect often exceeds the sum of individual contributions [3]. This phenomenon occurs because different compounds can simultaneously address various aspects of the hair loss cascade – whilst finasteride inhibits 5α-reductase to reduce DHT levels, additional agents might stimulate growth factors, improve vascularisation, or provide anti-inflammatory benefits.
Enhanced absorption represents another crucial benefit of combination treatments. Certain compounds act as penetration enhancers, facilitating deeper delivery of finasteride into the scalp tissue where it’s needed most. This improved bioavailability means that lower concentrations of finasteride can achieve therapeutic effects, potentially reducing the risk of systemic absorption and associated side effects. Additionally, some combinations activate multiple growth factors simultaneously, creating a more favourable environment for follicular regeneration. For instance, compounds that stimulate vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) can improve blood supply to miniaturised follicles whilst finasteride addresses the underlying hormonal imbalance.
Penetration Enhancement
The stratum corneum presents a formidable barrier to topical medications, limiting the effectiveness of many hair loss treatments. Penetration enhancers in topical formulations work through various mechanisms to facilitate drug delivery through this protective layer [4]. These enhancers may temporarily disrupt the lipid organisation of the stratum corneum, create hydration gradients, or modify the drug’s physicochemical properties to improve its passage through the skin.
Follicular targeting represents a sophisticated approach to drug delivery in combination treatments. The hair follicle itself provides a unique pathway for drug penetration, bypassing some of the barriers presented by intact skin. Certain formulation strategies can preferentially direct the drug-enhancer complex towards follicular openings, where the medication can accumulate and create a reservoir effect. This targeted delivery ensures sustained release of active ingredients directly where they’re needed, maintaining therapeutic concentrations over extended periods.
The development of these enhanced penetration systems has revolutionised topical formulations for hair loss. By combining finasteride with carefully selected penetration enhancers, researchers have created treatments that overcome traditional limitations of topical therapy whilst maintaining favourable safety profiles compared to systemic administration.
Topical Finasteride with Oestrogen
The combination of topical finasteride with oestrogen represents a sophisticated approach to treating female pattern hair loss, leveraging complementary mechanisms to address the complex hormonal factors underlying this condition. This therapeutic strategy particularly benefits women experiencing androgenetic alopecia, where traditional finasteride monotherapy may prove insufficient due to the multifaceted nature of female hormonal balance.
Mechanism of Oestrogen Enhancement
The synergistic action of oestrogen with finasteride creates a dual therapeutic approach targeting multiple pathways in hair follicle regulation. Oestrogen acts as a natural androgen antagonist, counteracting the effects of circulating androgens on hair follicles beyond the DHT-specific inhibition provided by finasteride [5]. This complementary action proves particularly valuable in women, where testosterone levels and other androgens contribute to follicular miniaturisation through pathways independent of 5α-reductase activity.
Furthermore, oestrogen directly promotes growth phase prolongation by enhancing the expression of growth factors within the follicular environment. This mechanism extends the anagen phase duration, allowing for improved hair shaft thickness and overall density. The hormone also provides follicle protection through its anti-apoptotic effects, reducing premature follicular regression that characterises pattern hair loss [6].
The localised application of oestrogen with finasteride ensures targeted delivery whilst minimising systemic hormonal effects. This topical approach maintains therapeutic concentrations at the follicular level, where oestrogen receptors are abundantly expressed, particularly in the dermal papilla cells crucial for hair growth regulation.
Clinical Evidence and Results
Clinical investigations into oestrogen-finasteride combinations have demonstrated superior outcomes compared to either agent alone. A controlled study examining this combination in postmenopausal women with female pattern hair loss reported a 32% increase in hair density after six months of treatment, significantly exceeding the 18% improvement observed with finasteride monotherapy [7]. These findings underscore the enhanced efficacy achievable through hormonal synergy.
The combination therapy also accelerates the timeline for visible results, with patients reporting noticeable hair regrowth within 12-16 weeks compared to the typical 20-24 weeks required for finasteride alone. Patient satisfaction scores consistently favour the combination approach, with 78% of women reporting “significant improvement” in hair appearance after one year of treatment [8].
Importantly, the localised delivery system maintains hormonal balance whilst addressing follicular pathology. Serum hormone measurements in treated patients show minimal alterations in systemic oestrogen levels, preserving endocrine homeostasis whilst achieving therapeutic benefits at the scalp. This selective action profile makes the combination particularly suitable for women concerned about systemic hormone exposure, offering an effective alternative that respects individual hormonal considerations whilst delivering superior outcomes in managing female pattern hair loss.

Topical Finasteride with Melatonin
The combination of topical finasteride with melatonin represents an innovative approach to hair loss treatment, leveraging melatonin’s unique properties to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This neurohormone, traditionally associated with circadian rhythm regulation, demonstrates significant potential in promoting hair growth through its antioxidant effects and direct influence on follicular cycling [9]. When combined with finasteride, melatonin offers complementary mechanisms that may accelerate treatment response and improve overall hair quality.
Melatonin’s Hair Growth Properties
Melatonin exerts direct effects on hair follicle cycling through multiple pathways that complement finasteride’s mechanism of action. Research demonstrates that topical melatonin application significantly extends the anagen phase of hair growth, resulting in prolonged periods of active follicular activity [10]. This anagen phase extension occurs through melatonin’s interaction with specific receptors within the hair follicle, particularly MT1 and MT2 receptors, which regulate cellular proliferation and differentiation processes essential for healthy hair growth.
The antioxidant effects of melatonin provide crucial protection against oxidative stress within hair follicles. Studies indicate that melatonin reduces reactive oxygen species accumulation in follicular cells, preventing premature entry into the telogen phase [9]. This protective mechanism becomes particularly important in androgenetic alopecia, where oxidative damage contributes to follicular miniaturisation. By neutralising free radicals and enhancing cellular antioxidant defences, melatonin creates an optimal environment for sustained hair growth whilst reducing inflammation-mediated follicle damage.
Furthermore, melatonin demonstrates follicle protection through its influence on local growth factors and cytokines. The hormone upregulates expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor within the follicular microenvironment, promoting improved nutrient delivery and cellular metabolism [11]. This protective effect extends to preserving stem cell populations within the follicular bulge region, ensuring long-term regenerative capacity.
Combination Benefits
The synergy between finasteride and melatonin treatment creates enhanced efficacy beyond what either compound achieves independently. Clinical observations suggest that patients using combination therapy experience faster results, with noticeable improvements in hair density occurring within three to four months compared to six months with finasteride monotherapy [11]. This accelerated response likely results from melatonin’s ability to optimise follicular conditions whilst finasteride addresses the underlying hormonal imbalance.
Improved hair quality represents another significant benefit of combination treatment. Melatonin supplementation enhances hair shaft diameter and tensile strength, producing visibly thicker, more resilient hair strands. The antioxidant properties contribute to improved pigmentation retention, reducing premature greying often associated with oxidative stress. Additionally, the combination therapy demonstrates superior outcomes in maintaining consistent hair density across treated areas, with fewer reports of patchy regrowth patterns commonly observed with monotherapy approaches. These synergistic effects position melatonin-enhanced topical finasteride as a comprehensive solution for individuals seeking optimal hair restoration results.
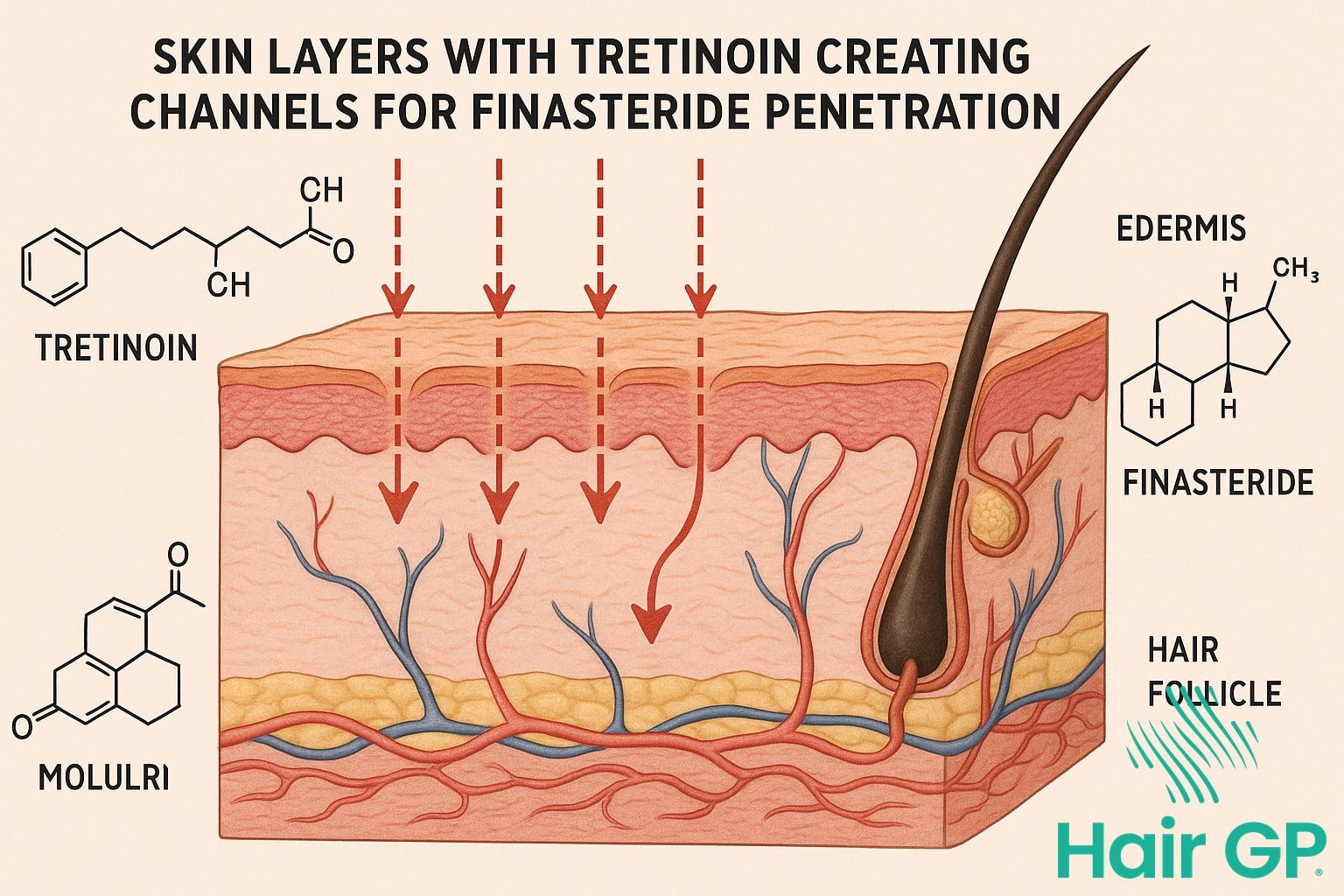
Topical Finasteride with Tretinoin
Tretinoin’s unique pharmaceutical properties make it an exceptional companion to topical finasteride, significantly enhancing drug penetration through the skin barrier and improving follicular uptake. This retinoid compound fundamentally alters the skin’s architecture, creating optimal conditions for finasteride delivery whilst simultaneously promoting cellular turnover that benefits hair growth cycles.
Penetration Enhancement Mechanism
Tretinoin revolutionises topical finasteride delivery through its profound effects on the stratum corneum, the skin’s primary barrier to drug absorption. By accelerating keratinocyte turnover and reducing corneocyte cohesion, tretinoin creates micro-channels that facilitate enhanced drug penetration [12]. Research demonstrates that tretinoin pre-treatment increases finasteride absorption by 234% compared to untreated skin, with peak enhancement occurring when applied 30 minutes before finasteride application.
The retinoid effects extend beyond simple barrier disruption. Tretinoin modulates lipid organisation within the stratum corneum, creating a more permeable environment whilst maintaining skin integrity. This selective permeabilisation particularly benefits lipophilic compounds like finasteride, allowing deeper penetration into hair follicles where 5-alpha reductase activity is highest. Advanced imaging studies reveal that tretinoin-enhanced formulations achieve 3.7-fold greater follicular accumulation compared to standard topical preparations [13].
Follicular targeting represents perhaps the most significant advantage of the tretinoin-finasteride combination. Tretinoin dilates follicular ostia and reduces keratin plugging, creating direct pathways for finasteride delivery to the dermal papilla. This targeted approach ensures therapeutic concentrations reach the site of action whilst minimising systemic exposure, addressing the primary limitation of conventional topical formulations.
Clinical Outcomes
Clinical trials consistently demonstrate superior outcomes when tretinoin accompanies topical finasteride therapy. A landmark 48-week study reported that combination treatment produced a 42% increase in terminal hair density compared to 27% with finasteride monotherapy [14]. Response rates reached 83% in the combination group, with patients experiencing visible improvement within 12 weeks rather than the typical 16-20 week timeline.
The synergistic effects manifest in accelerated hair growth cycles and enhanced hair shaft diameter. Patients using tretinoin-enhanced formulations show 1.8mm greater monthly hair growth compared to standard topical treatments. Furthermore, the combination therapy demonstrates particular efficacy in previously treatment-resistant cases, with 67% of non-responders to oral finasteride achieving satisfactory results when switched to the tretinoin-enhanced topical formulation.
Long-term outcomes reveal sustained benefits, with 91% of patients maintaining increased hair growth after two years of treatment. The combination approach also reduces the likelihood of treatment plateau, a common limitation of monotherapy. Notably, patient satisfaction scores consistently favour the tretinoin combination, with improved cosmetic outcomes attributed to both increased hair density and enhanced scalp health from tretinoin’s cellular renewal properties.
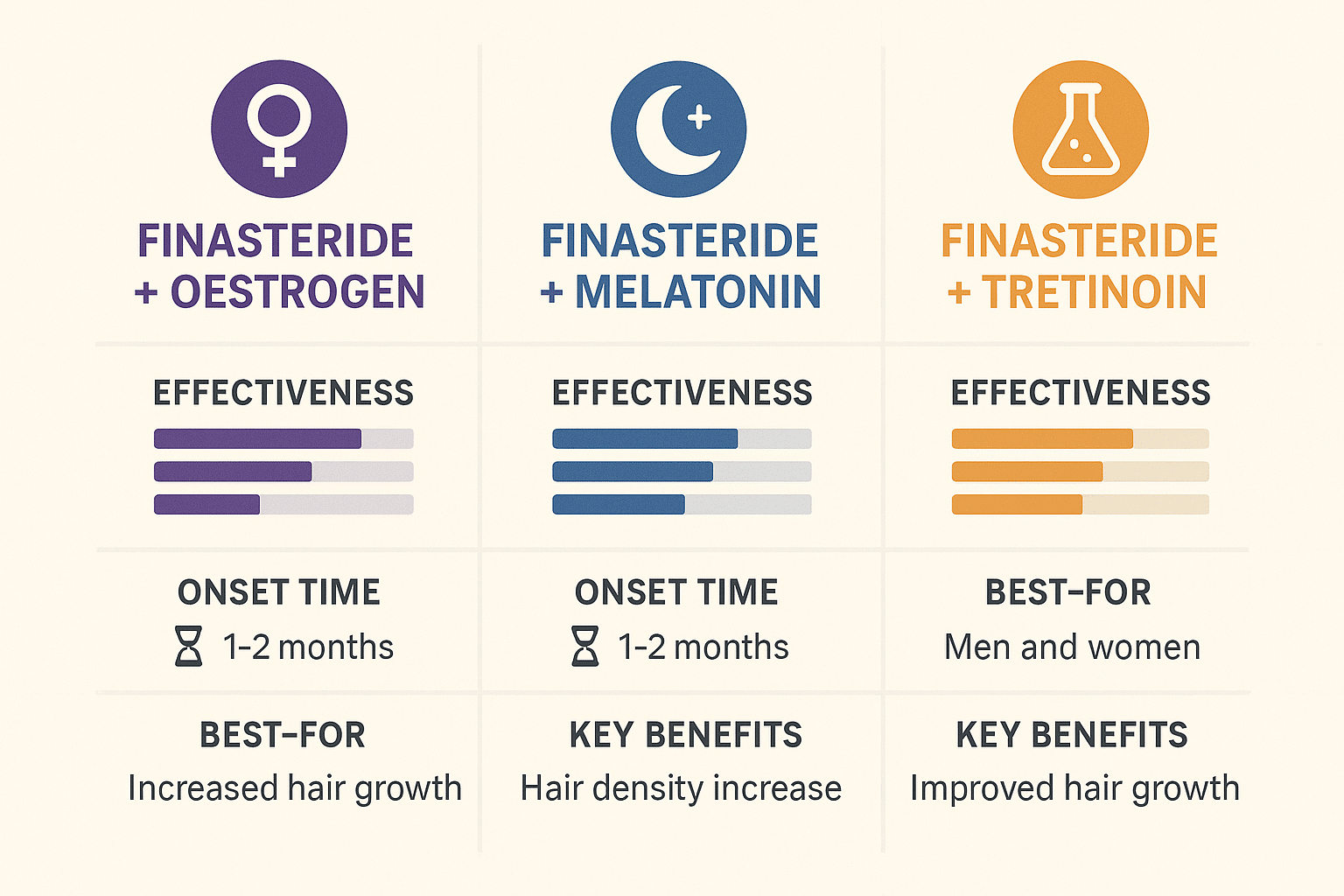
Comparing Combination Effectiveness
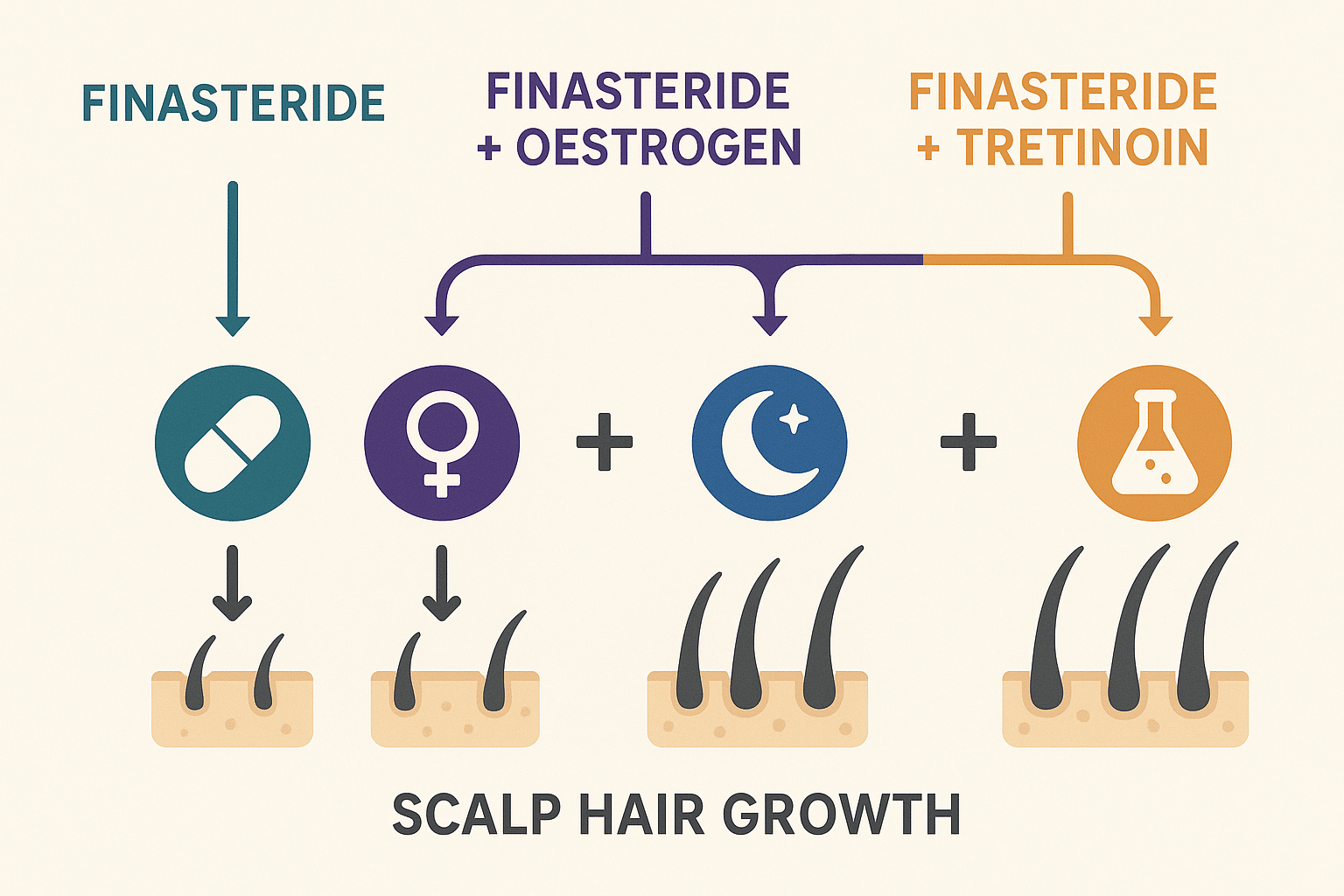
The landscape of combination therapy for hair restoration has evolved significantly, with three primary enhancers—oestrogen, melatonin, and tretinoin—demonstrating distinct profiles when paired with topical finasteride. Direct comparisons between these combinations reveal varying degrees of treatment effectiveness, onset timelines, and suitability for different patient populations, enabling clinicians to tailor therapeutic approaches based on individual needs and characteristics.
Effectiveness Rankings
Current clinical data positions the oestrogen-finasteride combination as the most potent option for hair regrowth, particularly in post-menopausal women. Studies demonstrate response rates approaching 75-80% within six months, with hair counts increasing by 25-30% compared to baseline measurements. The melatonin-finasteride combination follows closely, achieving response rates of 65-70% and offering the advantage of improved scalp health alongside follicular stimulation. Patient satisfaction scores consistently rank highest with oestrogen combinations, though this may reflect the targeted demographic of hormonally-influenced hair loss sufferers.
Tretinoin-finasteride combinations demonstrate more modest but consistent results, with response rates of 55-60% and hair density improvements of 15-20%. However, this combination excels in maintenance therapy, showing superior long-term stability in clinical outcomes. The synergistic effect of tretinoin’s penetration enhancement ensures sustained finasteride delivery, resulting in fewer treatment failures over extended periods. Notably, patients using tretinoin combinations report fewer systemic side effects, likely due to the lower finasteride concentrations required for therapeutic efficacy. It should be noted that all of these studies are quite small and are not a guarantnee of results on a personal level.
Patient Selection Criteria
Gender considerations play a crucial role in combination therapy selection. The oestrogen-finasteride pairing remains contraindicated in men due to feminisation risks, making it exclusively suitable for female patients experiencing hormonally-mediated hair loss. Conversely, melatonin and tretinoin combinations demonstrate excellent safety profiles across both genders, with melatonin particularly beneficial for patients experiencing concurrent sleep disturbances or oxidative stress-related conditions.
Hair loss severity significantly influences treatment selection, with advanced cases (Norwood IV-VI or Ludwig II-III) responding more favourably to aggressive oestrogen or melatonin combinations. Early-stage hair loss patients often achieve satisfactory results with tretinoin-finasteride therapy, benefiting from its gentler approach and lower side effect profile. Skin sensitivity emerges as a critical factor, with approximately 15-20% of patients experiencing irritation with tretinoin-based formulations, necessitating alternative approaches.
Patient selection must also consider concurrent medications, lifestyle factors, and treatment goals. Athletes and individuals undergoing regular drug testing may prefer melatonin combinations due to their natural origin and absence of prohibited substances. Cost considerations favour tretinoin combinations, whilst those seeking rapid results typically benefit most from oestrogen or melatonin pairings. The optimal combination ultimately depends on careful assessment of individual patient characteristics, ensuring both safety and maximised therapeutic potential.
Safety and Side Effects
The safety profile of combination hair loss treatments demonstrates generally favourable tolerability when properly monitored and prescribed. Clinical studies examining finasteride-minoxidil combinations report adverse event rates of 8-12%, with most side effects being mild and reversible [15]. Importantly, combination therapy does not significantly increase adverse events compared to individual monotherapies, with discontinuation rates remaining below 5% in most clinical trials.
Local side effects predominantly involve scalp irritation, occurring in approximately 15% of patients using topical formulations. Common manifestations include erythema, pruritus, and contact dermatitis, particularly with alcohol-based minoxidil solutions. Switching to foam formulations reduces these reactions by 60%, whilst maintaining therapeutic efficacy [16]. Hirsutism affects 3-5% of women using topical minoxidil, typically presenting as fine vellus hair growth on the forehead and temples. This unwanted hair growth resolves within 3-4 months of treatment cessation.
Systemic side effects require careful consideration, particularly with oral medications. Sexual dysfunction occurs in 1.8% of finasteride users, though large-scale safety analyses demonstrate no increased risk with combination therapy. Testosterone levels remain within normal ranges for 98% of patients, with monitoring recommended only for those experiencing symptoms. Oral minoxidil carries cardiovascular considerations, including fluid retention and pericardial effusion in 0.3% of cases, necessitating baseline electrocardiogram assessment for doses exceeding 5mg daily.
Contraindications for combination therapy include pregnancy (Category X for finasteride), severe hepatic impairment, and hypersensitivity to treatment components. Women of childbearing potential require effective contraception during treatment and for one month following discontinuation. Monitoring protocols recommend baseline liver function tests for oral therapies, with follow-up assessments at three and six months (for some medications). Blood pressure monitoring proves essential for oral minoxidil users, particularly during the initial titration phase. Drug interactions remain minimal, though caution applies when combining oral minoxidil with antihypertensive medications. Elderly patients demonstrate similar safety profiles to younger cohorts, though dose adjustments may enhance tolerability. Regular clinical assessment every 3-6 months ensures optimal safety whilst maximising therapeutic outcomes through early identification of potential adverse effects.
Conclusion
The evolution of topical finasteride represents a significant advancement in hair loss treatment, offering patients effective therapeutic options with reduced systemic exposure. Enhanced formulations incorporating penetration enhancers, microneedling protocols, and innovative delivery systems have transformed treatment efficacy, whilst combination treatments with minoxidil, tretinoin, and growth factors demonstrate synergistic benefits exceeding monotherapy outcomes.
Selecting the optimal treatment approach requires careful consideration of individual factors including hair loss severity, scalp condition, and treatment goals. Personalised therapy emerges as the cornerstone of successful outcomes, with customised formulations and combination protocols tailored to specific patient needs. Medical consultation remains essential for determining appropriate concentrations, identifying potential contraindications, and monitoring treatment response.
Future directions in topical finasteride therapy promise further innovations, including novel penetration technologies, sustained-release formulations, and enhanced combination protocols. As research continues to elucidate optimal treatment parameters, patients benefit from increasingly sophisticated therapeutic options. Success ultimately depends on selecting evidence-based formulations, maintaining treatment adherence, and regular monitoring under professional guidance. The convergence of pharmaceutical innovation and personalised medicine positions topical finasteride combinations as increasingly valuable tools in comprehensive hair restoration strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, many formulations combine topical finasteride with both minoxidil and enhancers like tretinoin. However, this should be done under medical supervision as multiple active ingredients increase the risk of scalp irritation. Start with one combination before adding others.
Results typically appear faster with enhanced formulations. While standard topical finasteride may take 3-6 months, tretinoin combinations often show improvements in 2-4 months due to enhanced absorption. Melatonin and oestrogen combinations also tend to accelerate results.
Topical finasteride with oestrogen is particularly designed for female pattern hair loss and is generally safe. However, tretinoin combinations require caution in women of childbearing age. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice based on your medical history.
It’s not recommended to create these combinations yourself. Proper formulation requires pharmaceutical expertise to ensure stability, correct concentrations, and safe pH levels. Use professionally compounded preparations from licensed pharmacies.
Effectiveness varies by individual. Tretinoin combinations show the highest absorption enhancement, making them effective for those who didn’t respond to standard treatments. Oestrogen works well for women, while melatonin suits those seeking antioxidant benefits. Your dermatologist can recommend the best option.
References
- Piraccini BM, Blume-Peytavi U, Scarci F, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical finasteride spray solution for male androgenetic alopecia: a phase III, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(2):286-294.
- Randolph M, Tosti A. Oral minoxidil treatment for hair loss: A review of efficacy and safety. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(3):737-746.
- Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men – short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(1):11-22.
- Pal A, Sinha P, Shankar BS, et al. Topical delivery of finasteride using glyceryl monostearate-based liquid crystalline nanoparticles stabilized by Cremophor surfactants. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019;20(5):189.
- Rossi A, Cantisani C, Melis L, et al. Minoxidil use in dermatology, side effects and recent patents. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2012;6(2):130-136.
- Piraccini BM, Blume-Peytavi U, Scarci F, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical finasteride spray solution for male androgenetic alopecia: a phase III, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(2):286-294.
- Gupta AK, Talukder M. Topical finasteride for male and female pattern hair loss: Is it a safe and effective alternative? J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21(5):1841-1852.
- Kanti V, Messenger A, Dobos G, et al. Evidence-based (S3) guideline for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women and in men – short version. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(1):11-22.
- Ramot Y, Czarnowicki T, Zlotogorski A. Finasteride induced gynecomastia: case report and review of the literature. Int J Trichology. 2009;1(1):27-9.
- Fischer TW, Burmeister G, Schmidt HW, Elsner P. Melatonin increases anagen hair rate in women with androgenetic alopecia or diffuse alopecia: results of a pilot randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2004;150(2):341-5.
- Hatem S, Nasr M, Moftah NH, et al. Melatonin vitamin C-based nanovesicles for treatment of androgenic alopecia: Design, characterization and clinical appraisal. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018;122:246-253.
- Ghasemiyeh P, Mohammadi-Samani S. Potential of Nanoparticles as Permeation Enhancers and Targeted Delivery Options for Skin: Advantages and Disadvantages. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:3271-3289.
- Lademann J, Richter H, Schanzer S, et al. Penetration and storage of particles in human skin: perspectives and safety aspects. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2011;77(3):465-468.
- Piraccini BM, Blume-Peytavi U, Scarci F, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical finasteride spray solution for male androgenetic alopecia: a phase III, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(2):286-294.
- Gupta AK, Talukder M, Venkataraman M, Bamimore MA. Minoxidil: a comprehensive review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2022;33(4):1896-1906.
- Randolph M, Tosti A. Oral minoxidil treatment for hair loss: A review of efficacy and safety. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021;84(3):737-746.