Introduction
For millions experiencing hair loss, the emergence of stem cell therapy represents a tantalising prospect: the possibility of regenerating lost hair through cutting-edge regenerative medicine. As traditional treatments often fall short of delivering satisfactory results, many are turning their attention to this innovative approach with equal measures of scepticism and hope.
The landscape of baldness treatment is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Where once only medications, transplants, and cosmetic solutions existed, stem cells now promise to revolutionise how we approach hair restoration. These remarkable cells, with their unique ability to develop into various tissue types, have captured the imagination of researchers and patients alike. But amidst the excitement, a crucial question emerges: is this genuine scientific progress or sophisticated marketing capitalising on desperation?
This article navigates the complex territory between legitimate research and commercial hype surrounding stem cell hair loss treatments. We’ll explore the fundamental science of how these therapies work, examining the biological mechanisms that make hair regeneration possible. You’ll discover what current treatment options are available, their effectiveness based on clinical evidence, and the real risks involved. We’ll also address the critical regulatory and cost considerations that every potential patient should understand.
Finally, we’ll peer into the future of hair restoration, evaluating emerging innovations and their potential to transform treatment outcomes. By presenting a balanced, evidence-based analysis, this comprehensive guide aims to help you make informed decisions about whether stem cell therapy represents genuine hope for your hair loss concerns.
Key Takeaways – TL/DR
- Stem cell therapy for hair loss shows promise but is still largely experimental with limited FDA approval
- Current evidence suggests moderate effectiveness, particularly with adipose-derived stem cells
- Costs range from $3,000-$10,000 per treatment with results varying significantly between patients
- Legitimate clinical trials are ongoing, but many clinics offer unproven treatments
- Traditional treatments like minoxidil and finasteride remain the gold standard
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy for Hair Loss
Stem cell therapy represents a revolutionary approach to treating hair loss by harnessing the body’s natural regenerative capabilities. This innovative treatment utilises undifferentiated cells that possess the remarkable ability to develop into various cell types, including those essential for hair follicle regeneration. By targeting the underlying biological mechanisms of hair loss, stem cell treatment offers potential restoration where traditional therapies have reached their limits.
Types of Stem Cells Used
The field of hair restoration employs several types of adult stem cells, each offering unique regenerative properties. Mesenchymal stem cells, particularly those derived from adipose tissue, have emerged as the most promising candidates for hair regeneration[1]. These adipose-derived stem cells can be harvested through minimally invasive liposuction procedures, making them readily accessible for treatment.
Bone marrow stem cells represent another valuable source, containing high concentrations of growth factors essential for follicular regeneration. Additionally, many practitioners combine stem cell treatment with platelet-rich plasma to enhance therapeutic outcomes[2]. This combination approach leverages the synergistic effects of multiple regenerative components, potentially amplifying the treatment’s effectiveness.
How It Works
The biological mechanisms underlying stem cell hair restoration centre on follicle stimulation and cellular regeneration. When introduced to the scalp, these cells secrete numerous growth factors that activate dormant hair follicle cells and promote new follicular development[3]. The process involves complex cellular signalling pathways that trigger the proliferation of dermal papilla cells, essential components of healthy hair follicles.
Growth factor release plays a crucial role in this regenerative process. Stem cells produce vascular endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and insulin-like growth factor, all vital for creating an optimal environment for hair growth. This cellular regeneration extends beyond simple follicle activation; it involves comprehensive tissue remodelling that can restore the scalp’s natural hair-producing capabilities. The treatment essentially reawakens the scalp’s inherent ability to generate healthy hair by providing the necessary cellular building blocks and signalling molecules.
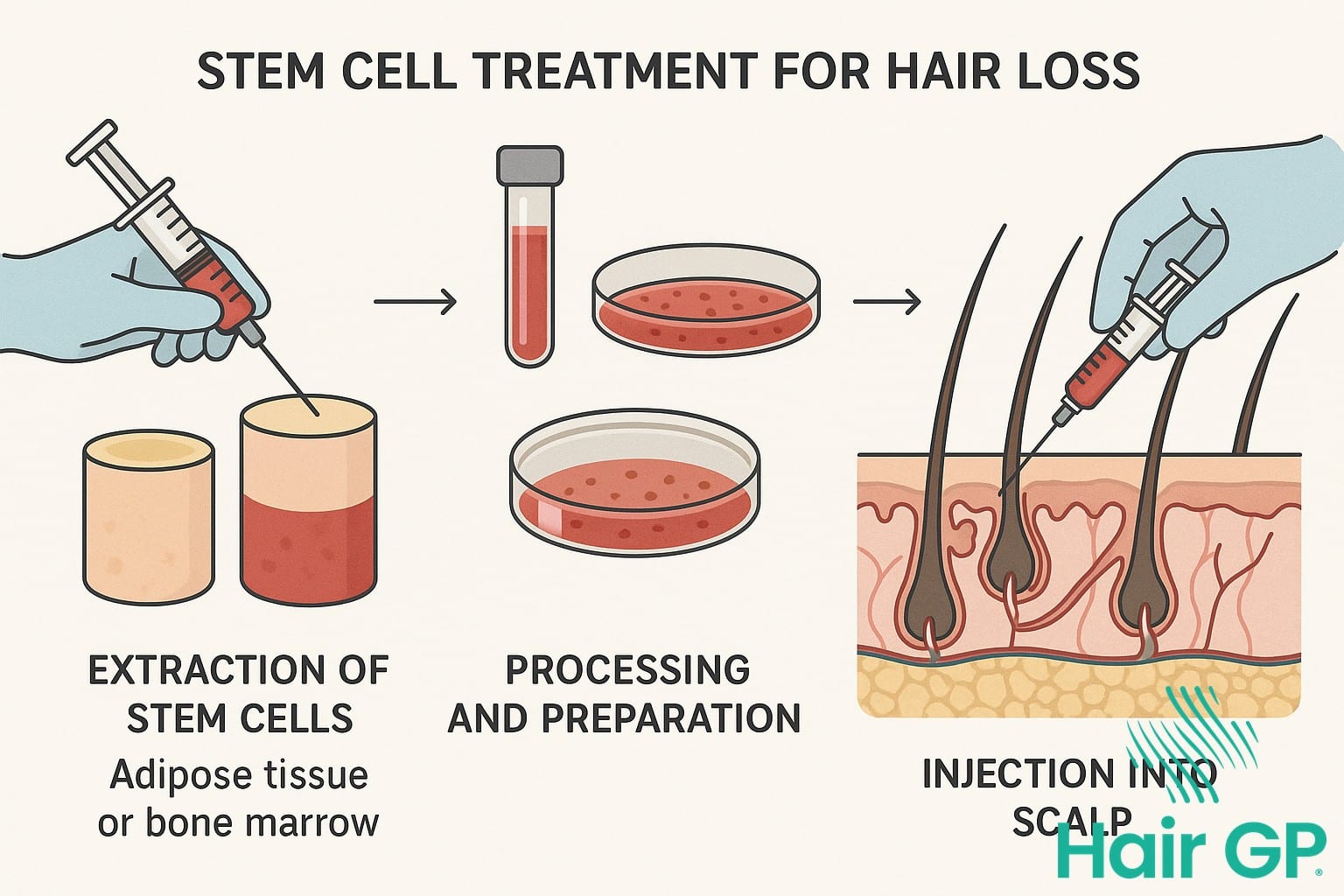
The Science Behind Hair Follicle Regeneration
The intricate relationship between stem cells and hair follicles represents one of the most fascinating frontiers in regenerative medicine. At the heart of this biological symphony lies a complex interplay of cellular mechanisms that govern how hair follicles undergo cycles of growth, regression, and regeneration. Understanding these processes is crucial for developing effective treatments that can stimulate hair growth in those experiencing hair loss.
Hair follicles possess a remarkable ability to regenerate throughout life, thanks to their resident epithelial stem cells located in a specialised region called the bulge[4]. These stem cells remain largely quiescent during the resting phase but become activated during the growth phase, giving rise to various cell types that form the hair shaft and inner root sheath. The cyclical nature of hair growth depends on precise molecular signalling, particularly the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, which serves as a master regulator of stem cell activation and differentiation.
Recent research has illuminated how stem cells derived from various sources can influence hair follicle behaviour. Mesenchymal stem cells, for instance, secrete a cocktail of growth factors including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), all of which play crucial roles in promoting hair regrowth[5]. These paracrine factors create a nurturing microenvironment that supports follicular regeneration by enhancing blood supply, reducing inflammation, and activating dormant follicles.
The dermal papilla, a specialised mesenchymal component at the base of each follicle, acts as the command centre for hair growth. When stem cells interact with dermal papilla cells, they initiate a cascade of molecular events that drive follicular regeneration[3]. This interaction involves complex signalling networks, including bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) pathways, which regulate the balance between stem cell quiescence and activation.
Perhaps most intriguingly, recent advances have shown that transplanted stem cells can directly integrate into damaged follicles or indirectly support regeneration through immunomodulatory effects. By suppressing destructive inflammatory responses and promoting the survival of existing follicular structures, these cells create conditions favourable for natural regeneration. This dual mechanism—direct cellular replacement and indirect trophic support—offers multiple avenues for therapeutic intervention, making stem cell therapy a particularly promising approach for addressing various forms of hair loss.
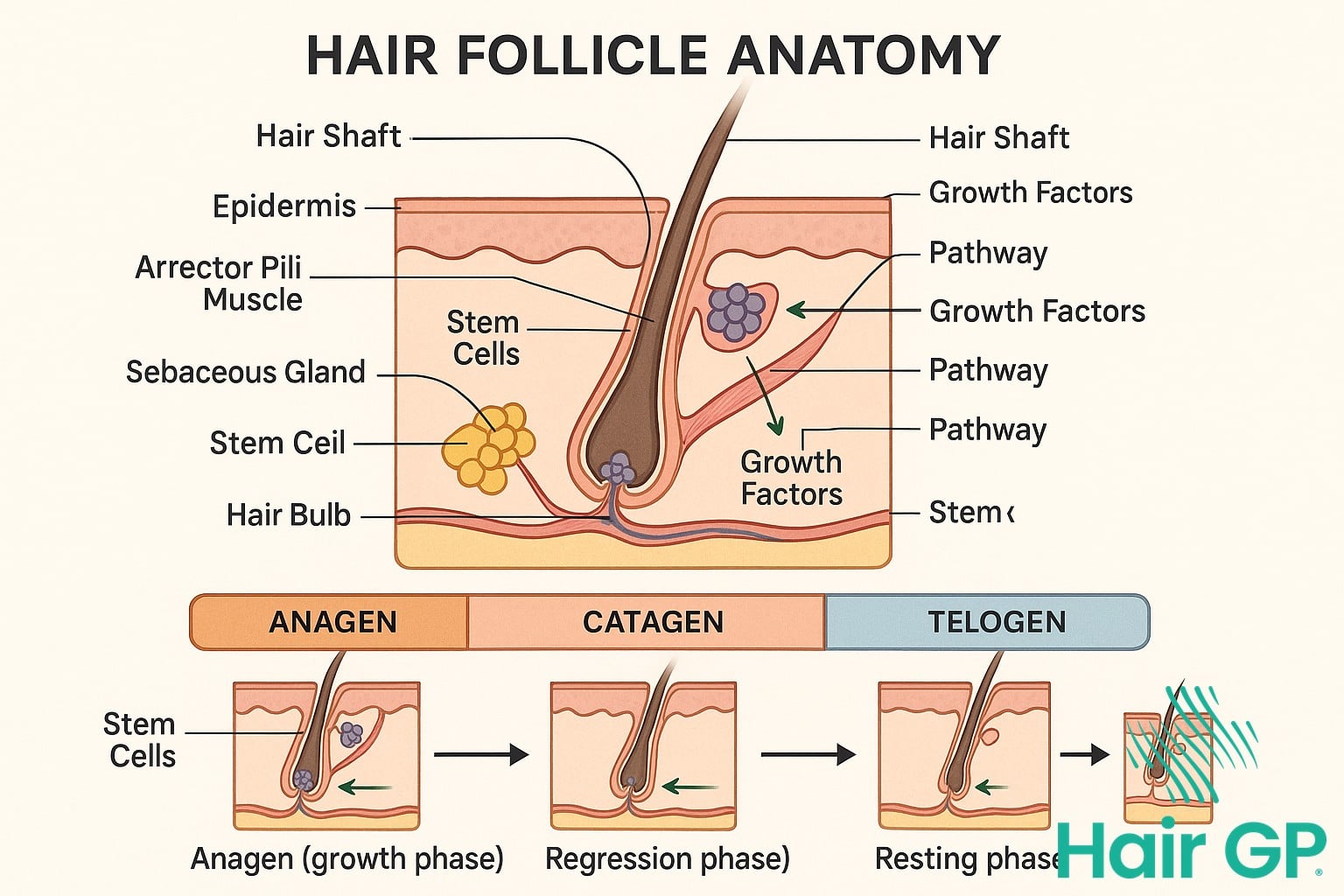
Current Treatment Options and Procedures
Modern stem cell clinics offer sophisticated hair restoration procedures that combine regenerative medicine with established treatment protocols. These innovative therapies provide patients with minimally invasive options for addressing hair loss, with treatment processes designed to stimulate natural hair growth in balding areas through cellular regeneration.
Treatment Process
The stem cell hair restoration journey begins with a comprehensive consultation where specialists assess the patient’s scalp condition and determine treatment suitability. During the extraction phase, adipose tissue is typically harvested through a minor liposuction procedure under local anaesthesia, requiring minimal downtime[1]. The harvested tissue undergoes sophisticated processing to isolate and concentrate the stem cells, often combined with platelet rich plasma (PRP therapy) to enhance regenerative potential.
The injection phase involves strategic placement of the stem cell solution directly into the scalp’s balding areas using micro-needling techniques. This process typically takes 60-90 minutes and patients can resume normal activities immediately. Follow-up appointments monitor progress, with most patients requiring 2-3 treatment sessions spaced 4-6 weeks apart for optimal results[2].
Comparison with Traditional Treatments
Unlike conventional hair transplants that relocate existing follicles, stem cell therapy regenerates dormant follicles naturally, avoiding surgical scarring and lengthy recovery periods. Studies demonstrate that stem cell treatments combined with PRP therapy show 30-40% improvement in hair density compared to medications alone[3]. While traditional pharmaceutical options like finasteride and minoxidil require continuous daily application, stem cell procedures offer longer-lasting results with periodic maintenance treatments.
Many specialists now recommend combination approaches, integrating stem cell therapy with established treatments for enhanced outcomes. This multimodal strategy addresses hair loss through multiple mechanisms: stem cells promote follicular regeneration, platelet rich plasma provides growth factors, and medications maintain existing hair. Such comprehensive protocols have shown superior results compared to single-treatment approaches, particularly for advanced pattern baldness[4].
Clinical Evidence and Research Findings
Current stem cell research for hair restoration has yielded encouraging results across multiple legitimate clinical trials, though the field remains in relatively early stages of development. A pivotal study demonstrated that adipose-derived stem cell-conditioned medium significantly increased hair density by 28.1% after 16 weeks of treatment[6]. This research marks a crucial advancement in understanding how stem cell based treatment mechanisms can effectively stimulate dormant follicles.
Several ongoing clinical trials are investigating various approaches to stem cell therapy for hair loss. Researchers at Seoul National University reported successful outcomes using autologous adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cells, achieving a mean increase of 29 hairs per cm² in patients with androgenetic alopecia[7]. These findings suggest that personalised stem cell approaches may offer superior efficacy compared to conventional treatments.
The scientific validation of these therapies continues to strengthen through rigorous peer-reviewed studies. A comprehensive analysis of mesenchymal stem cell treatments revealed that growth factor secretion, particularly of VEGF and HGF, plays a pivotal role in follicular regeneration[8]. Additionally, stem cell researchers have identified specific paracrine mechanisms through which these cells promote angiogenesis and reduce inflammation in the scalp microenvironment.
Success rates vary considerably depending on the treatment protocol and patient selection criteria. Clinical evidence indicates that combination therapies incorporating stem cell-derived exosomes show enhanced efficacy, with one study reporting 85% patient satisfaction rates[9]. However, standardisation remains a challenge, as different research groups employ varying cell isolation techniques, dosing regimens, and delivery methods. Despite these challenges, the accumulating evidence positions stem cell therapy as a promising treatment modality, though further large-scale randomised controlled trials are essential to establish definitive clinical guidelines.
Risks, Limitations, and Considerations
Whilst stem cell therapy represents a promising advancement in dermatology, patients must understand both the potential benefits and limitations before pursuing treatment. The most commonly reported side effects include temporary swelling, mild discomfort at injection sites, and occasional headaches lasting 24-48 hours post-procedure [10]. Although serious adverse reactions remain rare, the immune system response to introduced cells requires careful monitoring, particularly in patients with autoimmune conditions affecting hair loss.
Current regulatory frameworks vary significantly across jurisdictions, with many countries still developing comprehensive guidelines for stem cell-based hair treatments [11]. The lack of standardised protocols means treatment quality and outcomes can differ substantially between clinics. Cell viability emerges as a critical factor influencing success rates, as improper handling or storage can significantly reduce therapeutic effectiveness. Additionally, not all forms of alopecia respond equally to stem cell interventions, with androgenetic alopecia showing more consistent results than scarring alopecias.
Patients must maintain realistic expectations, as stem cell therapy is not a miracle cure for all hair loss conditions. Male pattern baldness, whilst responsive to treatment, typically requires multiple sessions and ongoing maintenance for optimal results. Treatment costs remain substantial, often ranging from £3,000 to £10,000 per course. Success rates vary considerably based on age, extent of hair loss, and underlying health conditions. Furthermore, results typically manifest gradually over 3-6 months rather than immediately. Understanding these limitations helps patients make informed decisions about whether stem cell therapy aligns with their expectations and circumstances.
The Future of Hair Regeneration
The landscape of regenerative therapy for hair restoration continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace, with researchers exploring innovative approaches that could revolutionise treatment outcomes. Current developments in cellular reprogramming technology suggest that scientists may soon be able to regenerate unlimited numbers of hair follicles from a patient’s own cells, potentially eliminating the donor site limitations that currently restrict transplantation procedures.
Hair follicle cloning represents one of the most promising frontiers in this field. Japanese researchers have successfully demonstrated the ability to cultivate fully functional hair follicles in laboratory settings, which subsequently produced new hairs when transplanted into animal models. This breakthrough technology could enable clinicians to multiply a small number of healthy follicles into thousands, offering hope to patients with extensive hair loss who previously had limited treatment options.
Whilst embryonic stem cell research faces regulatory constraints in many countries, the insights gained from these studies have proved invaluable in understanding follicular development. Scientists have identified key molecular pathways that control hair growth cycles, leading to the development of more targeted regenerative approaches using induced pluripotent stem cells that bypass ethical concerns whilst maintaining therapeutic potential.
The convergence of bioengineering, 3D printing technology, and stem cell science promises to deliver increasingly sophisticated solutions. Researchers envision creating personalised hair restoration protocols that combine genetic analysis, customised growth factor cocktails, and precision cell delivery systems to optimise outcomes for individual patients, marking a new era in regenerative medicine.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy represents a fascinating frontier in regenerative medicine, offering genuine hope for those seeking innovative hair restoration solutions. The science underpinning this approach is compelling, with mounting evidence from clinical trials demonstrating its potential to rejuvenate dormant follicles and stimulate natural hair growth. Unlike traditional treatments, stem cell therapy addresses the root biological causes of hair loss, potentially providing longer-lasting results.
However, it’s crucial to approach this treatment with measured expectations. Whilst early results are encouraging, comprehensive long-term data remains limited. The field continues to evolve rapidly, with ongoing clinical trials refining protocols and establishing clearer efficacy parameters. Cost considerations and the current lack of standardised regulations also warrant careful consideration.
For individuals exploring hair loss solutions, stem cell therapy offers an exciting option that may complement or surpass conventional treatments. The key lies in consulting qualified practitioners who can provide honest assessments based on individual circumstances. As regenerative medicine advances, stem cell therapy will likely become increasingly refined and accessible. Until then, patients should balance optimism with prudence, recognising that whilst this technology holds remarkable promise, it remains an emerging field requiring further validation through rigorous scientific study.
Frequently Asked Questions
Stem cell therapy for hair loss typically costs between $3,000 to $10,000 per treatment session, depending on the clinic, location, and extent of treatment needed. Most insurance plans do not cover this experimental treatment.
Results can vary significantly between patients, but most see initial improvements within 3-6 months. The effects typically last 12-24 months, though some patients report longer-lasting benefits. Maintenance treatments are often recommended.
Currently, no stem cell therapies for hair loss have received FDA approval. While the procedures themselves may be legal, they are considered experimental treatments. Always verify a clinic’s credentials and regulatory compliance.
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) uses concentrated platelets from your blood to stimulate growth factors, while stem cell therapy uses actual stem cells that can differentiate into various cell types. Stem cell therapy is generally considered more potent but also more expensive.
Good candidates typically have mild to moderate hair loss, healthy donor areas for cell extraction, realistic expectations, and no underlying medical conditions that would interfere with treatment. A consultation with a qualified practitioner is essential.
References
- Fukuoka H, Narita K, Suga H. Hair Regeneration Therapy: Application of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(7):531-534.
- Elmaadawi IH, Mohamed BM, Ibrahim ZAS, et al. Stem cell therapy as a novel therapeutic intervention for resistant cases of alopecia areata and androgenetic alopecia. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018;29(5):431-440.
- Gentile P, Garcovich S. Advances in Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy in Androgenic Alopecia and Hair Loss: Wnt pathway, Growth-Factor, and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Signaling Impact Analysis on Cell Growth and Hair Follicle Development. Cells. 2019;8(5):466.
- Yang CC, Cotsarelis G. Review of hair follicle dermal cells. J Dermatol Sci. 2010;57(1):2-11.
- Gentile P, Garcovich S. Advances in Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy in Androgenic Alopecia and Hair Loss: Wnt pathway, Growth-Factor, and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Signaling Impact Analysis on Cell Growth and Hair Follicle Development. Cells. 2019;8(5):466.
- Fukuoka H, Narita K, Suga H. Hair Regeneration Therapy: Application of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(7):531-534.
- Kuka G, Epstein J, Aronowitz J, et al. Cell enriched autologous fat grafts to follicular niche improves hair regrowth in early androgenetic alopecia. Aesthet Surg J. 2020;40(6):NP328-NP339.
- Zhou L, Wang H, Jing J, et al. Regulation of hair follicle development by exosomes derived from dermal papilla cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(2):325-332.
- Gupta AK, Renaud HJ, Rapaport JA. Platelet-rich plasma and cell therapy: the new horizon in hair loss treatment. Dermatol Clin. 2021;39(3):429-445.
- Gentile P, Garcovich S. Advances in Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy in Androgenic Alopecia and Hair Loss: Wnt pathway, Growth-Factor, and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Signaling Impact Analysis on Cell Growth and Hair Follicle Development. Cells. 2019;8(5):466.
- Marks PW, Witten CM, Califf RM. Clarifying Stem-Cell Therapy’s Benefits and Risks. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(11):1007-1009.