Introduction
The success of any hair transplant surgery fundamentally depends on one critical factor: your hair transplant donor area. This precious resource, typically located at the back and sides of your scalp, contains the genetically resistant hair follicles that will become the foundation of your restored hairline. Understanding how to maximise and preserve your donor supply is essential for achieving optimal results, both immediately and for years to come.
Effective donor area management goes far beyond simply extracting hair follicles. It requires a comprehensive approach that begins with thorough assessment and extends through careful surgical planning, precise extraction techniques, and diligent post-operative care. Whether you’re considering your first procedure or planning for future sessions, protecting this finite resource whilst maximising its potential is crucial for successful hair transplantation.
This guide will walk you through every aspect of optimising your donor resources. You’ll discover how to properly evaluate your donor area’s characteristics and capacity, learn about different extraction methods and their impact on preservation, and explore alternative donor sources when scalp hair alone isn’t sufficient. We’ll also cover essential post-procedure care protocols and long-term strategies to maintain donor health.
By understanding these principles, you’ll be better equipped to work with your surgeon in developing a personalised treatment plan that maximises your available resources whilst ensuring natural, lasting results. Whether you’re just beginning your hair restoration journey or seeking to optimise future procedures, mastering donor management is your key to long-term success.
Key Takeaways – TL/DR
- Proper donor area assessment determines the success and longevity of hair transplant results
- The safe donor zone typically contains 6,000-8,000 grafts for most patients
- Strategic extraction patterns preserve donor density while maximizing available grafts
- Body hair transplant can supplement scalp donor hair in suitable candidates
- Post-transplant care significantly impacts donor area recovery and future procedures
Understanding Your Donor Area
The donor area serves as the cornerstone of successful hair transplantation, containing follicles with unique genetic resistance to hair loss. This region, primarily located at the back and sides of the scalp, provides the hair characteristics that determine transplant longevity and aesthetic outcomes. Understanding the anatomical and biological properties of your donor hair enables better planning and more predictable results.
The Safe Donor Zone Explained
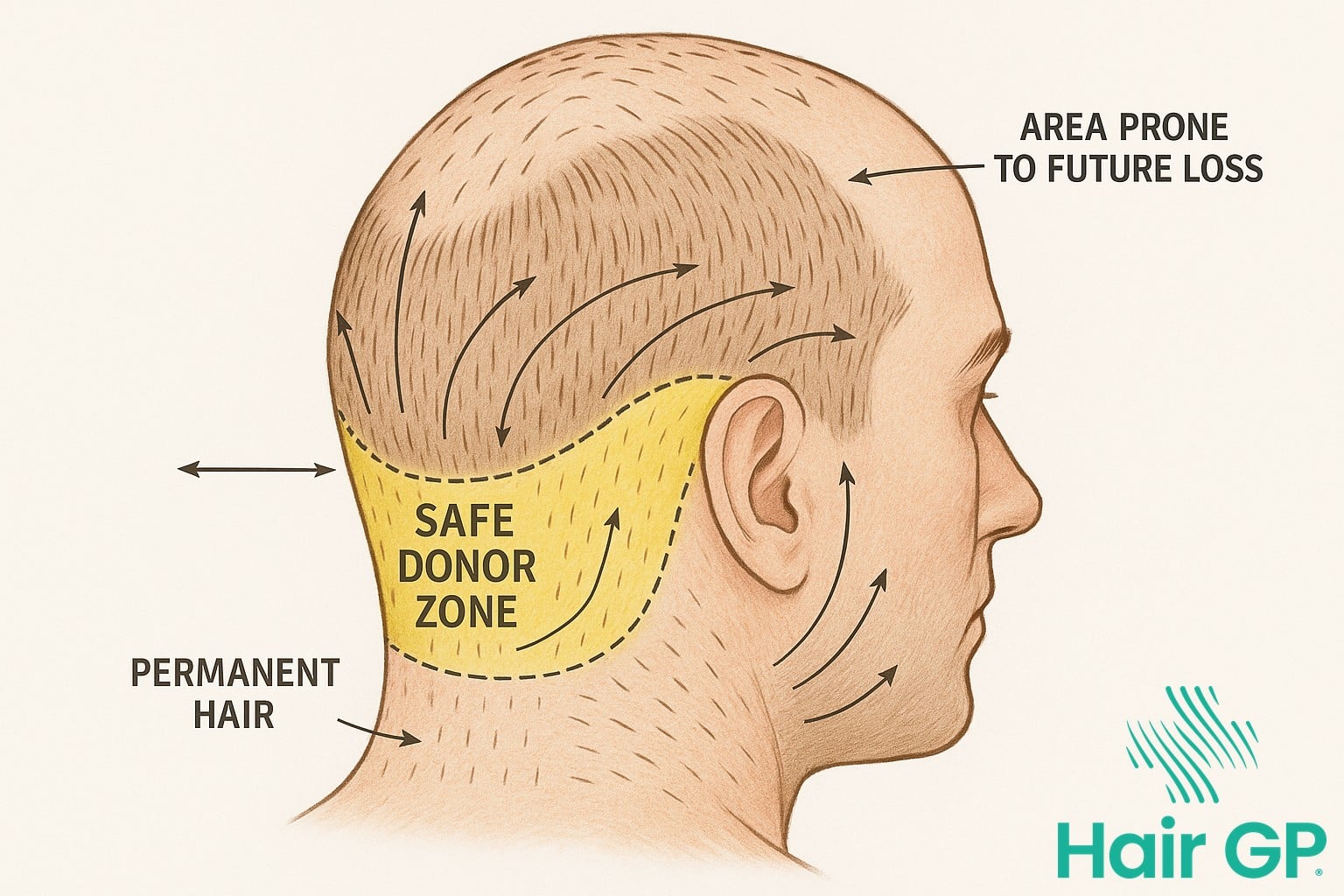
The safe donor zone represents a precisely defined area of the scalp where hair follicles exhibit remarkable resistance to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the primary hormone responsible for male pattern baldness [1]. This genetic programming ensures that donor hair maintains its growth characteristics even after transplantation to balding areas. The typical boundaries of this zone extend from approximately 2 centimetres above the ear level to the occipital protuberance, forming a horseshoe-shaped band measuring 12-15 centimetres in width [2].
The DHT resistance in these follicles stems from differences in androgen receptor expression and enzymatic activity compared to susceptible scalp regions. This inherent protection means transplanted hair continues growing throughout the patient’s lifetime, making donor area quality crucial for long-term success.
Assessing Hair Density and Quality
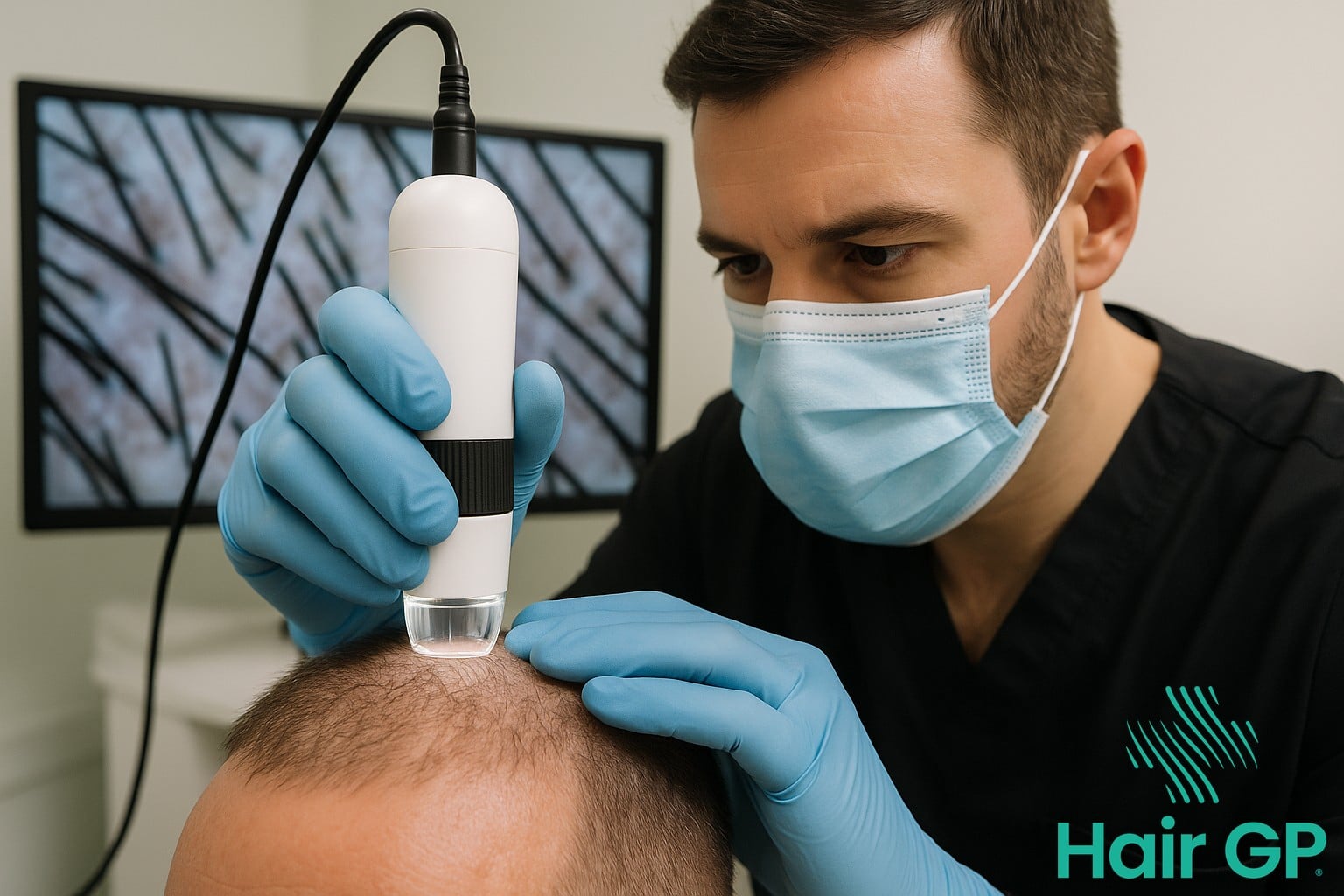
Evaluating overall hair density requires sophisticated measurement techniques to determine transplant feasibility. Practitioners typically use microscopy to assess density, which normally ranges from 60-100 follicular units per square centimetre in the donor zone. Hair calibre assessment involves measuring shaft diameter, with thicker hair providing superior coverage despite lower density.
Elasticity testing helps determine safe extraction limits, as tighter scalps may restrict harvesting capacity. These assessments collectively inform surgical planning, ensuring optimal use of available donor resources whilst maintaining natural appearance in both transplanted and donor regions.
Pre-Surgery Donor Area Assessment
A thorough donor area assessment forms the cornerstone of successful hair transplant planning, enabling your hair transplant surgeon to determine precisely how many grafts can be safely harvested whilst preserving a natural appearance. This comprehensive evaluation process involves sophisticated measurement techniques and careful analysis to ensure optimal outcomes for both immediate results and future considerations.
Hair Characteristics Analysis
The quality and characteristics of your available donor hair significantly influence transplant success. Hair shaft diameter serves as a crucial factor, with thicker follicles providing superior coverage despite requiring the same number of grafts . Curl pattern impacts visual density, as wavy or curly hair creates better coverage than straight hair due to its natural volume. Colour contrast between hair and scalp also affects perceived results, with lower contrast combinations typically yielding more favourable aesthetic outcomes.
Calculating Available Grafts
Determining available grafts requires precise donor density measurements using specialised instruments. The average donor area contains 60-100 follicular units per square centimetre [2]. Safe extraction typically limits harvest to 25-35% of total donor density to maintain natural appearance. For a standard donor area of 200 square centimetres with 80 units per square centimetre density, this translates to approximately 4,000-5,600 extractable grafts. Your surgeon must also factor in future hair loss progression, reserving adequate donor reserves for potential subsequent procedures whilst ensuring current aesthetic goals are achievable.
Extraction Techniques and Donor Preservation
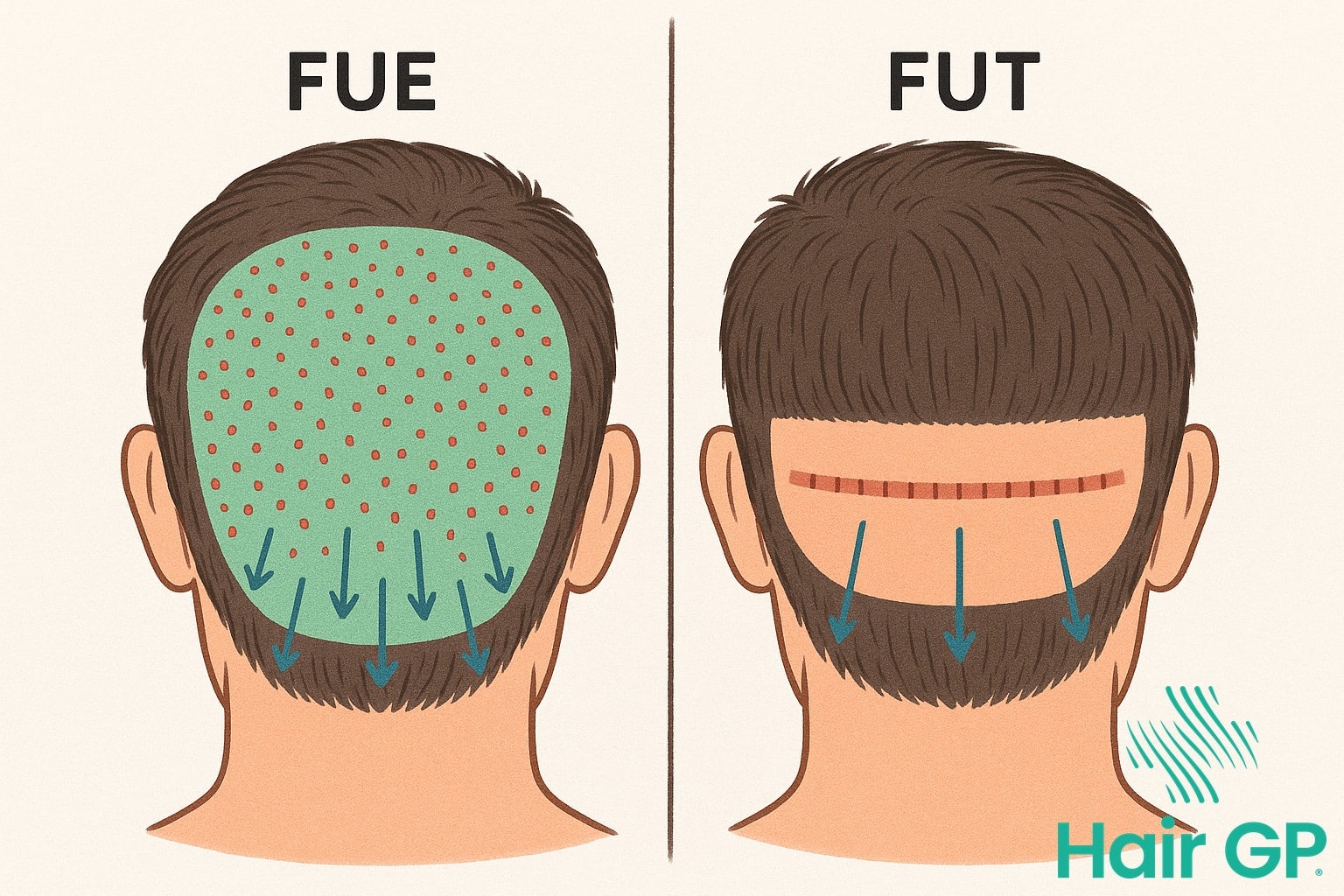
Modern extraction techniques play a crucial role in preserving donor resources for both immediate and future procedures. Understanding how follicular unit extraction (FUE) and follicular unit transplantation (FUT) impact the donor area enables surgeons to implement preservation strategies that maintain natural appearance whilst maximising available grafts.
Strategic Graft Distribution
When extracting hair follicles, an experienced surgeon employs specific patterns to ensure even distribution throughout the donor area. Skip pattern extraction involves harvesting every third or fourth follicular unit, leaving neighbouring units intact to maintain visual density. This technique prevents over-harvesting in concentrated areas that could create visible thinning.
Zone rotation during graft harvesting distributes extraction across multiple donor regions rather than depleting a single area. By alternating between upper, middle, and lower safe zones, surgeons preserve overall density whilst obtaining the required number of grafts. This approach proves particularly valuable for patients requiring multiple procedures over their lifetime.
Preserving Donor Density
Maintaining the donor area’s appearance requires strict adherence to extraction limits. Research indicates that removing more than 25-30% of follicular units per square centimetre risks visible thinning[1]. Most experienced surgeons limit extraction to 15-20% to ensure natural density remains post-procedure.
Camouflage techniques further protect donor aesthetics. These include strategic placement of extraction sites behind the temporal ridge and maintaining a buffer zone above the occipital protuberance. Long-term planning considers future hair loss patterns, preserving grafts in stable areas for potential future procedures.
Whether utilising follicular unit extraction or follicular unit transplantation, successful donor preservation depends on methodical planning and conservative extraction practices. These strategies ensure patients maintain natural-looking donor areas whilst achieving optimal transplant results.
Alternative Donor Sources
When traditional scalp donor follicles prove insufficient, body hair transplant options provide valuable alternatives for hair restoration procedures. Body hair from beard, chest, and other areas can supplement limited scalp supply, though careful assessment ensures optimal outcomes.
Beard and Body Hair Viability
Assessment criteria for alternative donor sources focus on growth characteristics and compatibility. Body hair exhibits distinct growth cycles, with anagen phases typically shorter than scalp hair [3]. Texture matching remains crucial, as beard hair often provides the closest resemblance to scalp characteristics. Survival rates for body hair grafts vary, with beard follicles demonstrating 80-90% viability whilst chest hair shows lower rates [4]. Careful selection based on calibre, curl pattern, and growth rate optimises results.
Integration Strategies
Successful integration requires strategic placement and mixing ratios. Hair transplantation specialists typically reserve body hair for crown areas where texture differences prove less noticeable. Mixing ratios of 70:30 scalp to body hair maintain natural appearance. Direct hair implantation techniques facilitate precise placement, allowing surgeons to blend different hair types seamlessly. Aesthetic considerations include gradual transition zones and strategic positioning to maximise coverage whilst maintaining natural density patterns throughout the recipient area.
Post-Transplant Donor Management
Proper donor area management following a transplant procedure plays a crucial role in healing success and preserving options for future treatments. Understanding both immediate and long-term care protocols ensures optimal recovery whilst maintaining the integrity of remaining scalp tissue for potential subsequent procedures.
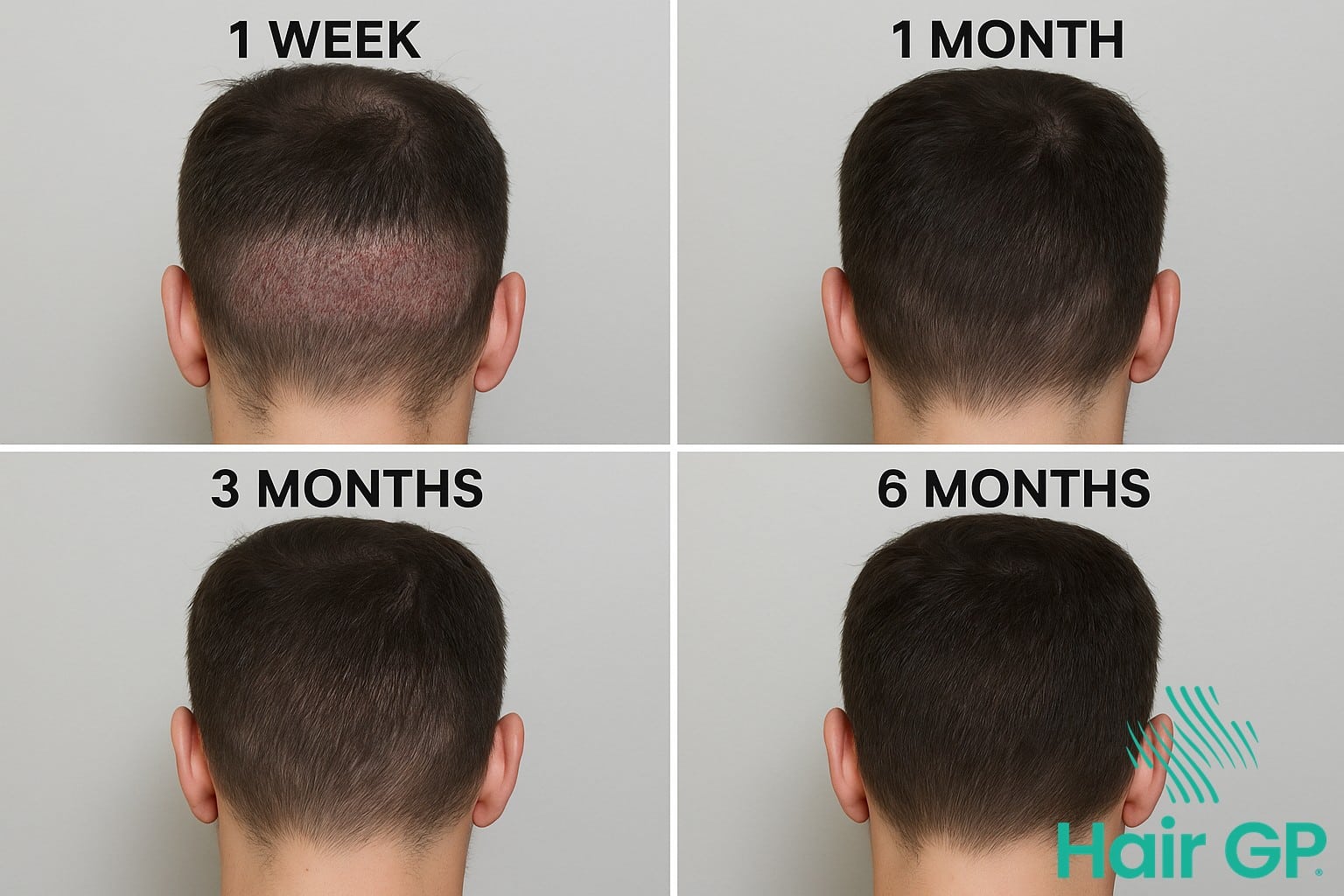
Immediate Recovery Protocol
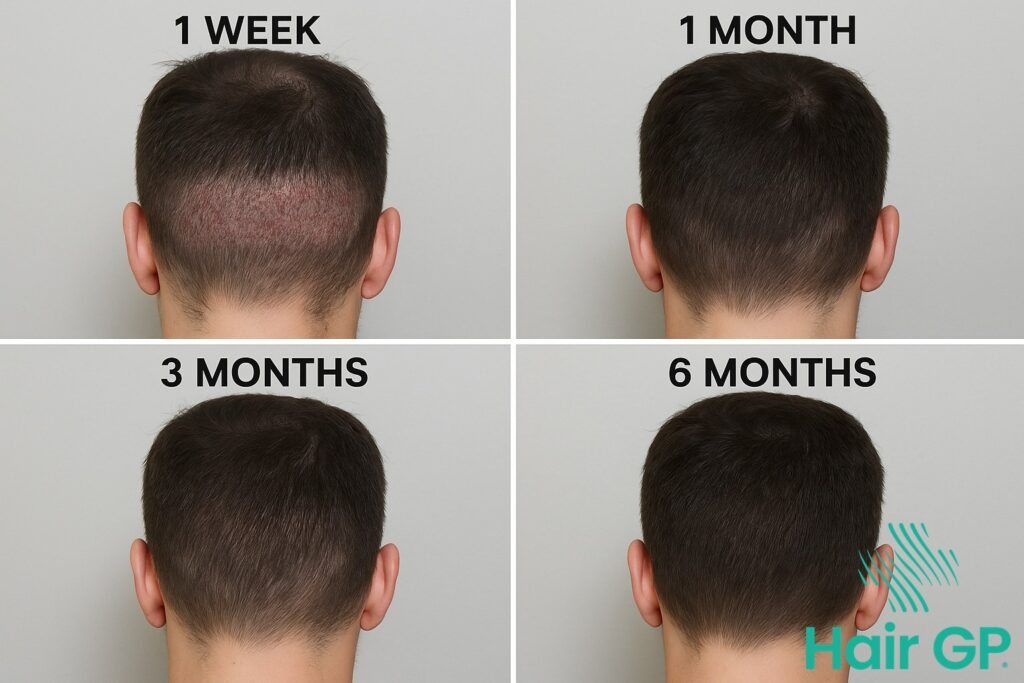
The first fortnight after surgery requires diligent post transplant care to support graft survival and donor zone healing. Gentle cleaning begins 48 hours post-procedure using lukewarm water and careful dabbing motions, avoiding direct pressure or rubbing. Activity restrictions include avoiding strenuous exercise, swimming, and direct sun exposure during this critical period. Signs of proper healing include minimal swelling, gradual scab formation that naturally falls away within 7-10 days, and absence of excessive redness or discharge. Most patients experience temporary numbness in the donor area, which typically resolves within three to six months as nerve endings regenerate.
Long-term Maintenance
Ongoing donor area care supports hair regrowth and maintains scalp health for years following surgery. Regular scalp treatments using gentle, sulphate-free products help maintain optimal tissue condition without disrupting healing follicles. Light circular massage techniques, starting three weeks post-procedure, improve blood circulation and reduce any residual tightness. Monitoring changes involves observing hair density patterns, checking for any unusual thinning, and noting texture changes that might indicate compromised scalp tissue. Annual assessments with your surgeon help track donor area recovery and determine viability for future procedures if needed.
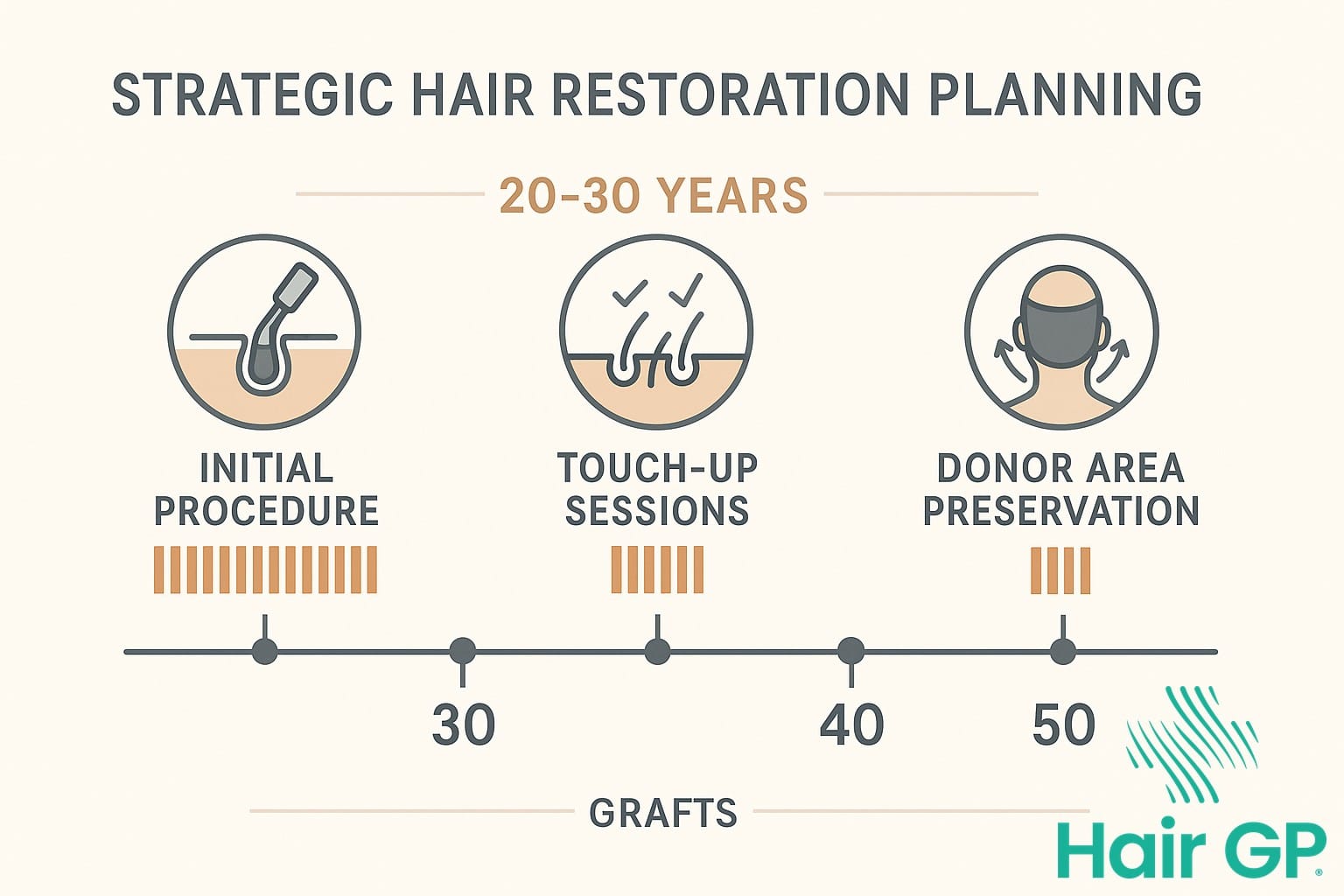
Optimizing Long-Term Results
Achieving successful hair transplantation outcomes requires strategic planning that extends beyond a single procedure. A comprehensive hair restoration journey typically involves mapping potential future hair loss patterns and allocating donor grafts accordingly. Experienced surgeons develop personalised treatment plans that reserve sufficient donor resources for potential future needs, ensuring patients maintain natural-looking results throughout their lives.
Maintaining donor area health between procedures proves essential for long-term success. Regular scalp care, proper nutrition, and avoiding harmful styling practices help preserve the integrity of remaining follicles. Patients who follow post-operative care guidelines and attend regular follow-up appointments typically experience better hair transplant results over time.
Partnering with skilled surgeons who understand donor management principles significantly impacts long-term outcomes. These professionals carefully calculate extraction patterns during each hair restoration surgery, preserving density whilst maximising graft yield. By employing advanced techniques and conservative extraction strategies during each hair transplant procedure, they ensure patients retain adequate donor reserves for future treatments, ultimately leading to sustainable, natural-looking results that stand the test of time.
Conclusion
Effective donor area management forms the cornerstone of successful hair transplantation. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored critical principles that protect your hair transplant donor area whilst maximising graft yield. From proper extraction techniques that preserve surrounding follicles to strategic planning that accounts for future hair loss, each aspect contributes to optimal outcomes.
The longevity of transplanted hair follicles depends significantly on how well your donor area is managed before, during, and after hair surgery. Maintaining appropriate extraction densities, respecting anatomical boundaries, and implementing proper healing protocols ensure your donor area remains healthy for potential future procedures.
Perhaps most crucially, selecting an experienced surgeon who understands individual variations in donor characteristics makes the difference between adequate and exceptional results. Skilled practitioners customise extraction patterns based on your unique hair characteristics, scalp laxity, and long-term goals, ensuring hair grafts are harvested sustainably.
Remember, successful donor management isn’t just about today’s procedure—it’s about preserving options for tomorrow. By following evidence-based protocols and working with qualified professionals who prioritise long-term donor health, you’re investing in results that stand the test of time.
Frequently Asked Questions
The safe extraction limit varies by individual but typically ranges from 4,000-6,000 grafts for FUE procedures, depending on donor density, scalp laxity, and hair characteristics. An experienced surgeon can assess your specific capacity.
With proper extraction techniques and staying within safe limits, the donor area should maintain a natural appearance. Strategic extraction patterns and respecting density thresholds prevent visible thinning.
No, extracted follicles do not regenerate. However, surrounding hair can compensate for properly distributed extractions, maintaining overall appearance. This is why strategic planning is crucial.
Body hair has different growth characteristics and typically lower survival rates than scalp hair. It’s best used as a supplementary source when scalp donor supply is limited, not as a primary option.
Most surgeons recommend waiting 12-18 months between procedures to allow complete healing and accurate assessment of results. This timeline ensures optimal donor area recovery and planning for subsequent sessions.
References
- Inui S, Fukuzato Y, Nakajima T, Yoshikawa K, Itami S. Androgen-inducible TGF-beta1 from balding dermal papilla cells inhibits epithelial cell growth: a clue to understand paradoxical effects of androgen on human hair growth. FASEB J. 2002. PMID: 12397096
- Jimenez F, Alam M, Vogel JE, Avram M. Hair transplantation: Basic overview. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33905785
- Umar S. Body Hair Transplant by Follicular Unit Extraction: My Experience With 122 Patients. Aesthet Surg J. 2016. PMID: 27241361
- Umar S. The transplanted hairline: leg room for improvement. Arch Dermatol. 2012. PMID: 22351827