Introduction
For many women, menopause brings unexpected changes beyond hot flushes and mood swings—thinning hair, receding hairlines, and overall changes in hair texture can become distressing realities. Hormonal hair loss during this life stage affects up to 40% of women, making it one of the most common yet under-discussed aspects of the menopausal transition.
The good news is that hormone replacement therapy (HRT) offers promising solutions for maintaining and restoring hair health during menopause. Understanding how different HRT options impact your hair can help you make informed decisions that support both your overall wellbeing and your confidence in your appearance.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricate relationship between hormones and hair growth, examining why menopausal hair loss occurs and how various hormone therapies can help address these challenging changes. We’ll delve into the science behind hormonal fluctuations and their effects on hair follicles, comparing different HRT formulations and their specific benefits for hair preservation and regrowth.
You’ll discover how delivery methods—from transdermal patches to oral tablets—can influence hair health outcomes, and learn practical strategies to maximise your treatment’s hair-protective effects. We’ll also provide realistic timelines for seeing improvements and guidance on when professional intervention may be necessary.
Whether you’re experiencing early signs of hormonal hair loss or seeking to prevent future thinning, this article will equip you with evidence-based information to discuss with your healthcare provider, helping you choose the most hair-friendly approach to hormone replacement therapy for your individual needs.
Key Takeaways – TL/DR
- Oestrogen is always hair-friendly but the Progesterone component can sometimes not be so it’s key to pick the right formulation with your Doctor.
- Transdermal delivery methods may offer better hair protection than oral hormone therapy
- Bioidentical hormones can provide more predictable hair health outcomes for many women
- Combining HRT with targeted hair care strategies maximizes protective benefits
Understanding Menopausal Hair Loss
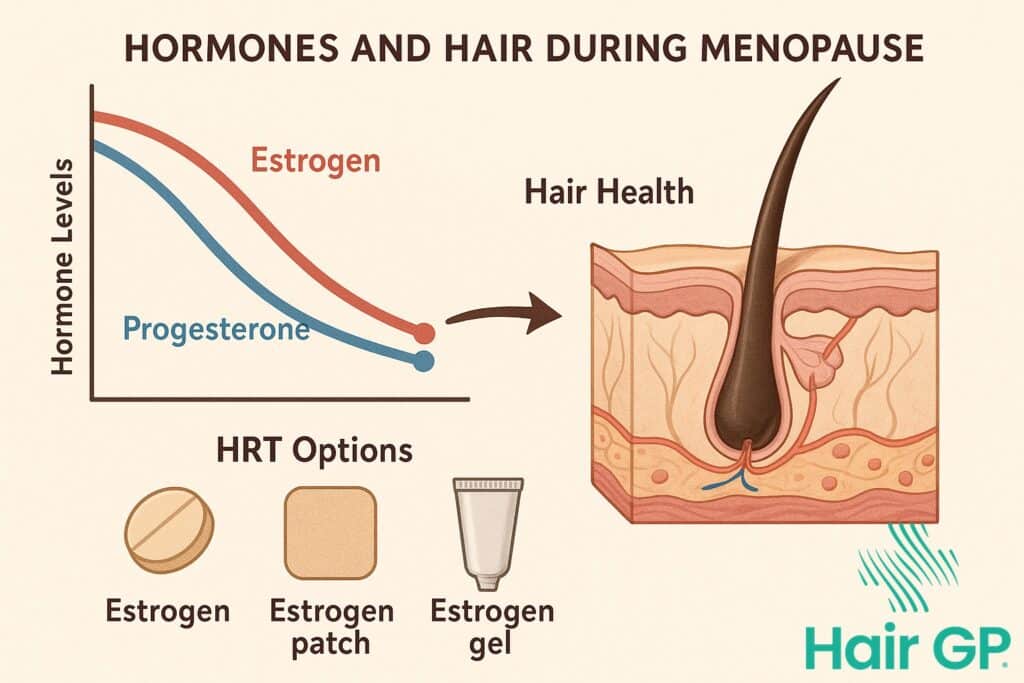
During menopause, declining oestrogen levels trigger complex biological changes that significantly impact hair health. Research indicates that up to 50% of women experience noticeable hair thinning by age 50, with menopausal hormonal shifts being a primary contributing factor [1]. The reduction in oestrogen removes its protective effects on hair follicles, whilst simultaneously allowing androgens like dihydrotestosterone (DHT) to exert greater influence on hair growth cycles.
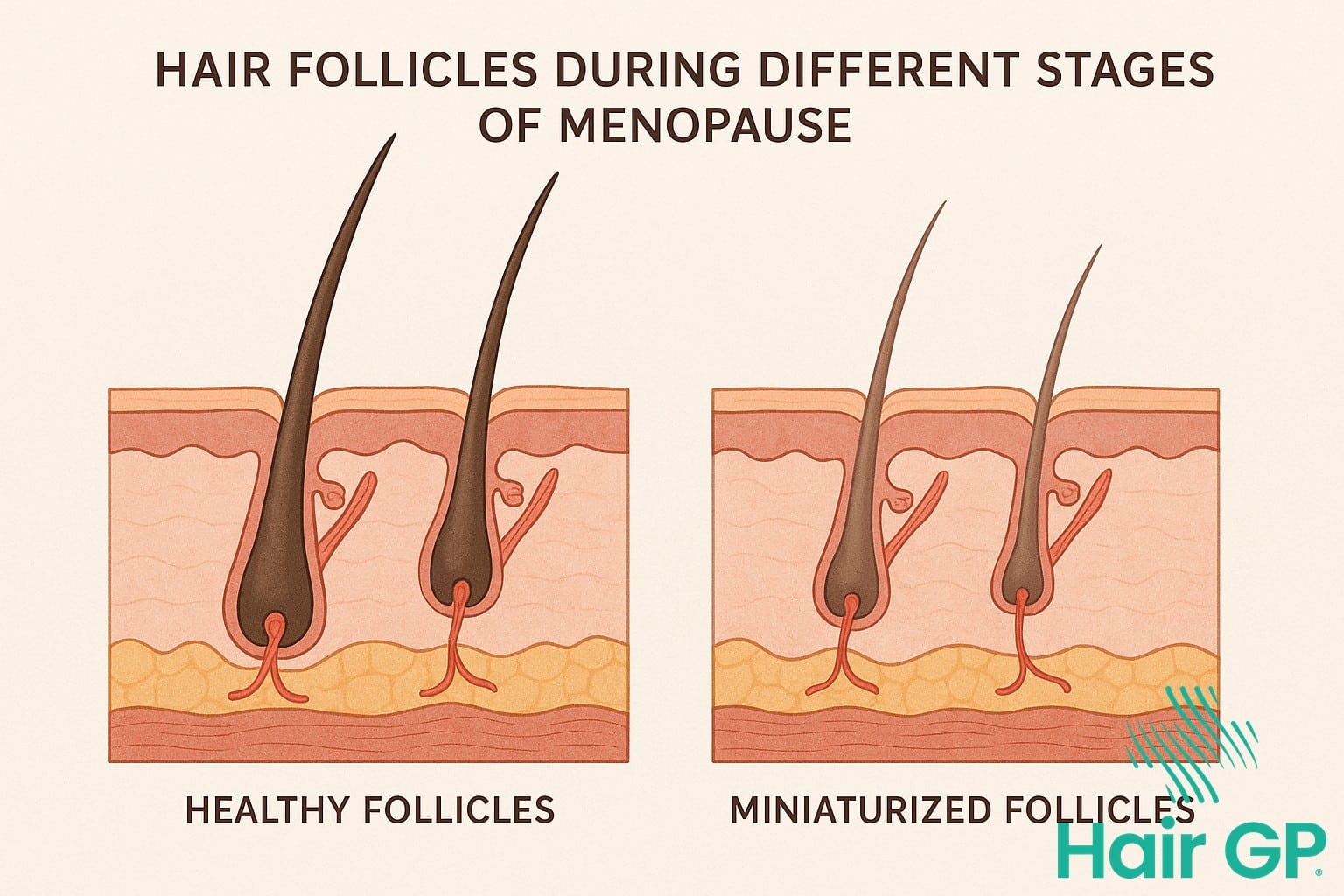
Two distinct patterns emerge during this transition. Androgenetic alopecia, commonly known as female pattern hair loss, manifests as diffuse thinning across the crown and top of the scalp, affecting the hair follicles’ ability to produce thick, healthy strands [2]. This condition occurs when hair follicles become increasingly sensitive to DHT, causing them to shrink progressively with each growth cycle.
Simultaneously, many women experience telogen effluvium, characterised by increased hair shedding as more follicles enter the resting phase prematurely. Unlike androgenetic alopecia’s gradual progression, telogen effluvium can cause sudden, widespread hair thinning across the entire scalp. The hormonal fluctuations during perimenopause and menopause disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, pushing follicles into dormancy and reducing the overall density and quality of hair production throughout this transitional period.
How Hormones Impact Hair Growth Cycles
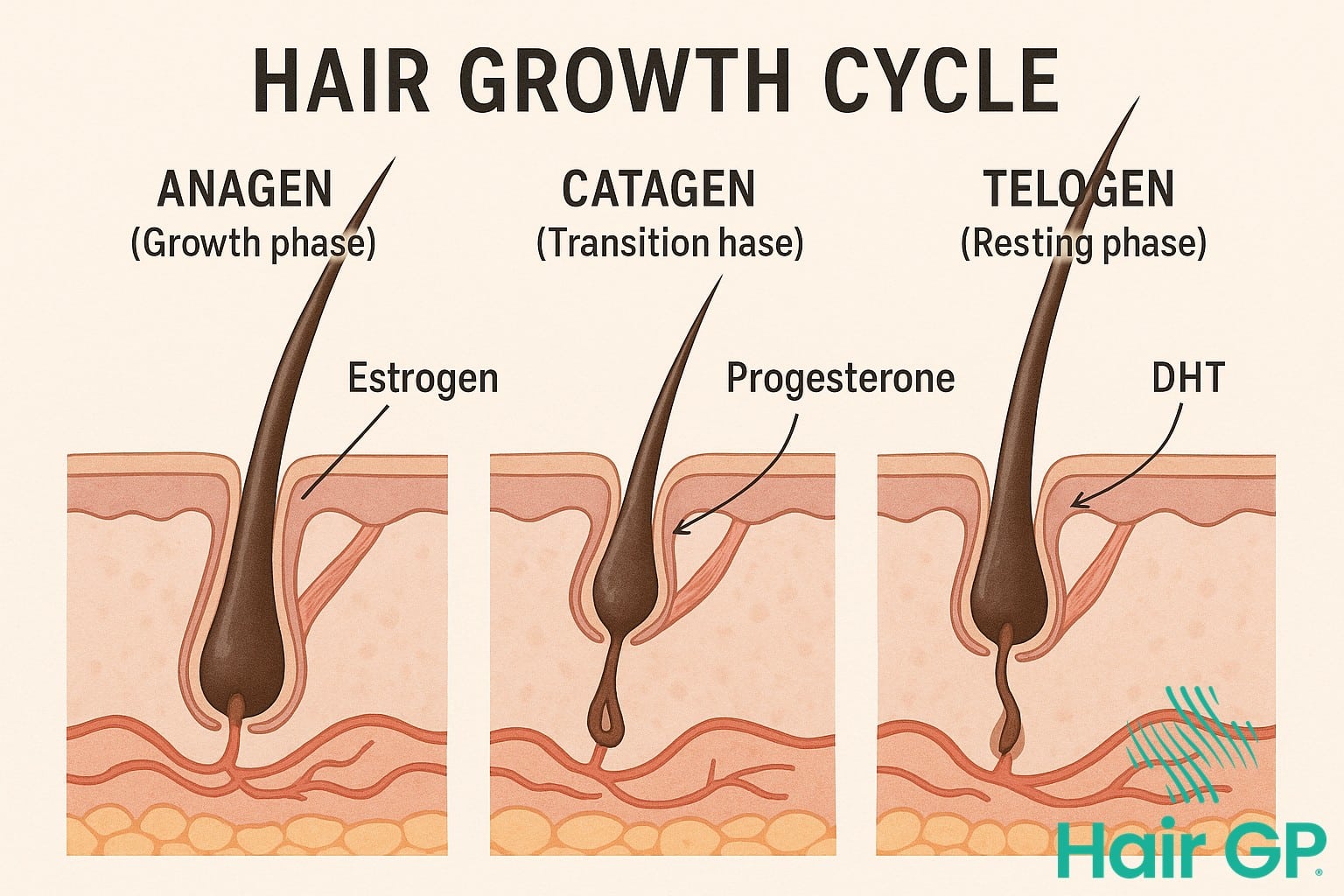
The hair growth cycle operates through three distinct phases: anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (resting). Hormonal fluctuations significantly influence these phases, with oestrogen playing a crucial protective role in maintaining healthy hair follicles and extending the anagen phase [3]. During reproductive years, elevated oestrogen levels promote hair density by prolonging growth phases and strengthening follicular structures.
Conversely, androgens, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), exert opposing effects on hair follicles. DHT binds to androgen receptors in susceptible follicles, triggering a process called miniaturisation where follicles progressively shrink and produce finer, shorter hairs [4]. This mechanism underlies pattern hair loss in genetically predisposed individuals.
As oestrogen levels decline during menopause, the protective influence on hair follicles diminishes whilst androgen activity becomes relatively more pronounced. This hormonal shift disrupts the normal hair growth cycle, shortening anagen phases and increasing telogen duration. The resulting imbalance manifests as reduced hair density, increased shedding, and changes in hair texture. Progesterone also contributes by modulating androgen receptor sensitivity, though its role remains less well-characterised than estrogen’s protective effects.
Hair-Friendly HRT Formulations
Different HRT formulations offer varying levels of hair protection, with careful selection crucial for managing menopausal symptoms whilst preserving hair health. Understanding the specific impacts of oestrogen-only therapy, combined HRT, and bioidentical hormones helps determine the most suitable hair friendly hormone approach for individual needs.
Oestrogen-Only Therapy Benefits
Oestrogen-only HRT provides the strongest hair protective effects by maintaining optimal estrogen levels without introducing potentially androgenic compounds [5]. This formulation however can ONLY be used by those who have undergone a hysterectomy. If you still have your womb then you ALWAYS need to combine oestrogen with progesterone to mimise the risk of Endometrial Cancer.
Oestrogen only formulations benefits women who have undergone hysterectomy, as it eliminates concerns about endometrial stimulation whilst maximising hair preservation benefits. The absence of synthetic progestins means minimal androgenic activity, allowing estrogen’s hair-protective properties to work unimpeded. Estrogen therapy directly supports hair follicle health by extending the anagen growth phase and maintaining hair shaft diameter, making it an excellent choice for those primarily concerned with hair thinning during menopause.
Combined HRT Considerations
Combined HRT requires careful progestin selection, as different synthetic progestins exhibit varying degrees of androgenic activity that can counteract oestrogen’s hair benefits [6]. Progestins like medroxyprogesterone acetate possess stronger androgenic properties compared to micronised progesterone or dydrogesterone, potentially contributing to hair loss rather than prevention. Bioidentical hormones, particularly micronised progesterone, offer a more hair-friendly approach within combined therapy regimens.

Delivery Methods and Hair Health
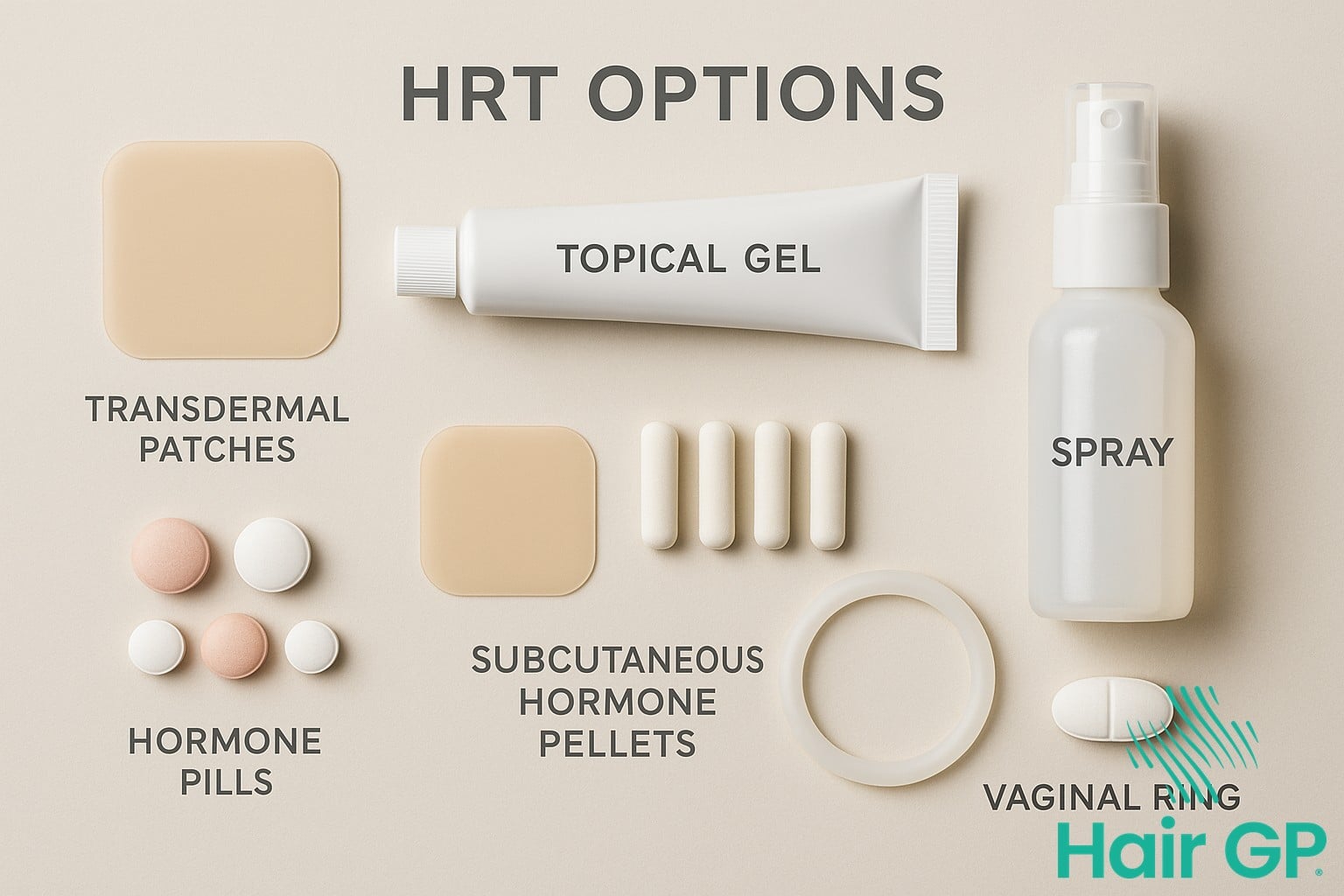
The method of hormone replacement therapy delivery significantly influences oestrogen absorption patterns and subsequent effects on hair density and scalp health. Transdermal patches and gels provide steady hormone release, avoiding the dramatic peaks and troughs associated with oral medications that can trigger hormonal shifts detrimental to hair follicle stability . This consistent delivery mechanism helps maintain optimal oestrogen levels for supporting hair growth cycles whilst minimising the metabolic processing that occurs with oral administration.
Transdermal systems demonstrate superior bioavailability compared to oral formulations, as they bypass first-pass liver metabolism and deliver hormones directly into systemic circulation . This enhanced absorption translates to more stable oestrogen concentrations, which research indicates may better preserve hair density during menopausal transitions. The steady hormonal environment created by transdermal delivery helps counteract the adverse effects of declining oestrogen on hair follicle miniaturisation.
Clinical evidence suggests that women using transdermal oestrogen therapy experience fewer fluctuations in hormone levels that can disrupt hair growth phases. The consistent absorption profile supports scalp health by maintaining protective hormonal influences on hair follicles, potentially offering superior outcomes for hair preservation compared to intermittent oral dosing schedules that create cyclical hormonal variations.
Supporting Hair Health During HRT
While HRT provides hormonal support for hair health, complementary strategies can significantly enhance these benefits. Addressing nutritional deficiencies plays a crucial role in supporting healthy hair growth, as deficiencies in iron, zinc and vitamin D can disrupt the hair cycle regardless of hormonal status. A balanced diet rich in protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants provides essential building blocks for strong, resilient hair.
Lifestyle factors equally influence hair health outcomes during HRT. Regular exercise improves blood circulation to the scalp, while stress management techniques help prevent cortisol-induced hair loss. Quality sleep supports the natural hair cycle, allowing follicles to repair and regenerate effectively.
Gentle hair care practices complement hormonal therapy by minimising mechanical damage. Using mild shampoos, avoiding excessive heat styling, and protecting hair from environmental stressors preserve the improvements gained through HRT. These holistic approaches not only optimise hair health but also boost self esteem as women experience visible improvements in hair quality and density.
Timeline and Realistic Expectations
Understanding the natural hair growth cycle helps set realistic expectations when starting HRT for hair health. Since hair grows approximately 1.2cm per month, visible improvements in hair quality typically become apparent after 3-6 months of consistent treatment. Individual responses vary significantly based on factors including age, underlying health conditions, stress levels, and the severity of initial hair loss.
The first signs of treatment success often include reduced hair shedding and improved hair texture rather than immediate regrowth. Many women notice their existing hair feels stronger and appears shinier within the first few months. Fuller hair and noticeable improvements to improve hair density generally require 6-12 months of treatment, as the hair growth cycle must complete its phases. Patience remains essential, as sustainable hair health improvements develop gradually rather than dramatically, with peak benefits often occurring after one year of consistent HRT therapy.
When to Seek Professional Guidance
Seek immediate consultation with healthcare providers if you experience sudden, patchy hair loss, which may indicate alopecia areata or other serious autoimmune conditions requiring specialised medical treatment. Rapid hair loss accompanied by scalp irritation, redness, or scarring also warrants urgent medical attention from qualified healthcare professionals.
A GP specialising in hair disorders can provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment options beyond standard HRT therapy. These specialists may recommend complementary therapies such as topical minoxidil for enhanced hair regrowth or finasteride in specific cases where clinically appropriate. Healthcare providers can also assess whether underlying medical conditions like thyroid disorders or nutritional deficiencies contribute to ongoing hair loss problems.
Professional guidance ensures safe treatment combinations and careful monitoring for potential interactions between HRT and other hair loss treatments, optimising therapeutic outcomes whilst minimising health risks.
Conclusion
The relationship between hormone replacement therapy and hair health during menopause requires careful consideration and personalised approaches. Throughout this discussion, we’ve established that not all HRT formulations affect healthy hair equally, with some options proving more beneficial than others for maintaining hair density and quality.
Choosing the right hormone replacement therapy involves understanding how different formulations interact with your unique hormonal profile. Oestradiol-based treatments, particularly when combined with hair-friendly progestogens like micronised progesterone, often provide superior outcomes for hair health compared to synthetic alternatives. However, what works optimally for one woman may not be ideal for another, highlighting the critical importance of individualized treatment plans.
Working closely with knowledgeable healthcare providers ensures that your menopause management strategy addresses both systemic health concerns and aesthetic priorities like hair preservation. Regular monitoring allows for adjustments that can optimise both overall wellbeing and hair health outcomes.
Remember that maintaining healthy hair during menopause is achievable with the right approach. By understanding your options, advocating for hair-conscious treatment choices, and embracing individualized treatment strategies, you can navigate this hormonal transition whilst preserving the hair health that contributes to your confidence and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Oestrogen-dominant formulations, particularly transdermal delivery methods, tend to be most hair-friendly. Bioidentical hormones with natural progesterone are generally preferable to synthetic progestins for hair health.
Most women notice reduced hair shedding within 3-6 months of starting HRT, with visible hair density improvements typically occurring after 6-12 months of consistent treatment.
HRT can help stabilize hair loss and improve hair quality, but significant regrowth of lost hair is less common. Earlier intervention generally yields better results for hair preservation.
References
- Fabbrocini G, Cantelli M, Masarà A, Annunziata MC, Marasca C, Cacciapuoti S. Female pattern hair loss: A clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic review. Int J Womens Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 30627618
- Ohnemus U, Uenalan M, Inzunza J, Gustafsson JA, Paus R. The hair follicle as an estrogen target and source. Endocr Rev. 2006. PMID: 16877675
- Kaufman KD. Androgens and alopecia. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12573818
- Randolph JF, Zheng H, Sowers MR, Crandall C, Crawford S, Gold EB et al.. Change in follicle-stimulating hormone and estradiol across the menopausal transition: effect of age at the final menstrual period. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21159842
- Baber RJ, Panay N, Fenton A. 2016 IMS Recommendations on women's midlife health and menopause hormone therapy. Climacteric. 2016. PMID: 26872610
- L'hermite M, Simoncini T, Fuller S, Genazzani AR. Could transdermal estradiol + progesterone be a safer postmenopausal HRT? A review. Maturitas. 2008. PMID: 18775609