Introduction
The internet is awash with claims linking celibacy to improved hair growth and enhanced testosterone levels, but what does the science actually say? Many men experiencing male pattern baldness have encountered suggestions that periods of abstinence might slow hair loss or even promote regrowth. These assertions often stem from the belief that sexual activity depletes vital nutrients or hormones essential for healthy hair.
Understanding the relationship between celibacy and hormone levels requires examining the complex interplay between testosterone, its derivatives, and hair follicle health. Whilst testosterone levels may fluctuate during periods of abstinence, the mechanisms behind hair growth and loss are far more intricate than simple hormone availability.
This article provides a comprehensive, evidence-based examination of these popular claims. We’ll explore how testosterone actually affects hair follicles and investigate whether celibacy produces meaningful changes in hormone levels over time. The role of genetics versus lifestyle factors in male pattern baldness will be examined, alongside common misconceptions about sexual behaviour and hair loss.
We’ll also address frequently cited myths about excessive sexual activity causing hair thinning, reviewing what research reveals about these persistent beliefs. Finally, we’ll consider the broader health implications of extended celibacy, weighing potential benefits against possible drawbacks to provide a balanced perspective on this lifestyle choice and its effects on overall wellbeing.
Key Takeaways – TL/DR
- Celibacy may cause temporary testosterone increases but doesn’t significantly improve long-term hormone levels
- Hair loss is primarily genetic and DHT-related, not directly influenced by ejaculation frequency
- Excessive masturbation claims about hair loss lack scientific support
- Health benefits of celibacy are limited and don’t include improved hair growth
The Science Behind Testosterone and Hair Growth
Understanding the complex relationship between testosterone and hair loss requires examining the intricate biological processes that govern hair follicle function. As the primary male sex hormone, testosterone undergoes enzymatic conversion to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which directly influences hair growth patterns and contributes to male pattern baldness through specific cellular mechanisms.
How Testosterone Affects Hair Follicles
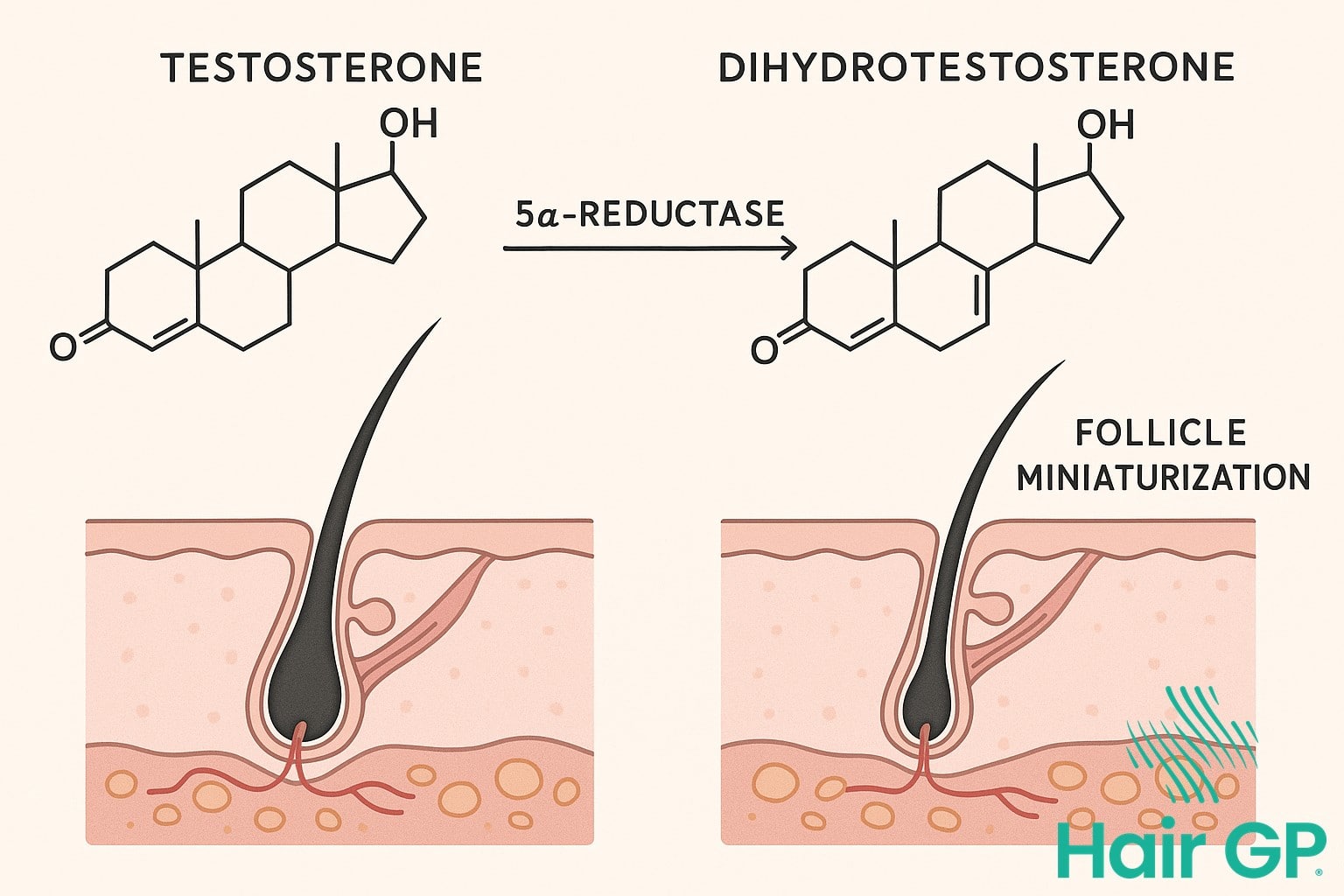
The conversion of testosterone to DHT occurs through the enzyme 5α-reductase, with DHT levels being approximately 10 times more potent than testosterone in binding to androgen receptors [1]. When DHT binds to androgen receptors located within hair follicles, it triggers a process called follicle miniaturisation, where healthy terminal hairs progressively shrink into fine, weak vellus hairs. This binding process is particularly pronounced in genetically susceptible areas of the scalp, including the crown and hairline regions. The miniaturisation occurs gradually over multiple hair growth cycles, with each successive hair becoming thinner and shorter until the follicle eventually ceases producing visible hair. Serum testosterone levels themselves don’t directly correlate with hair loss severity; rather, it’s the local conversion to DHT and the sensitivity of individual hair follicles that determines the extent of hair loss [2].
The Role of Genetics in Male Pattern Baldness
Genetic predisposition plays the decisive role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to DHT-induced hair loss. The inherited sensitivity of androgen receptors varies significantly between individuals, explaining why some men maintain thick hair despite normal testosterone levels whilst others experience significant hair loss. Family history patterns, particularly from the maternal line, strongly predict hair loss likelihood, though paternal genetics also contribute. Age-related progression typically begins in the twenties or thirties, with hair follicles gradually becoming more sensitive to DHT over time, leading to the characteristic patterns of male pattern baldness.
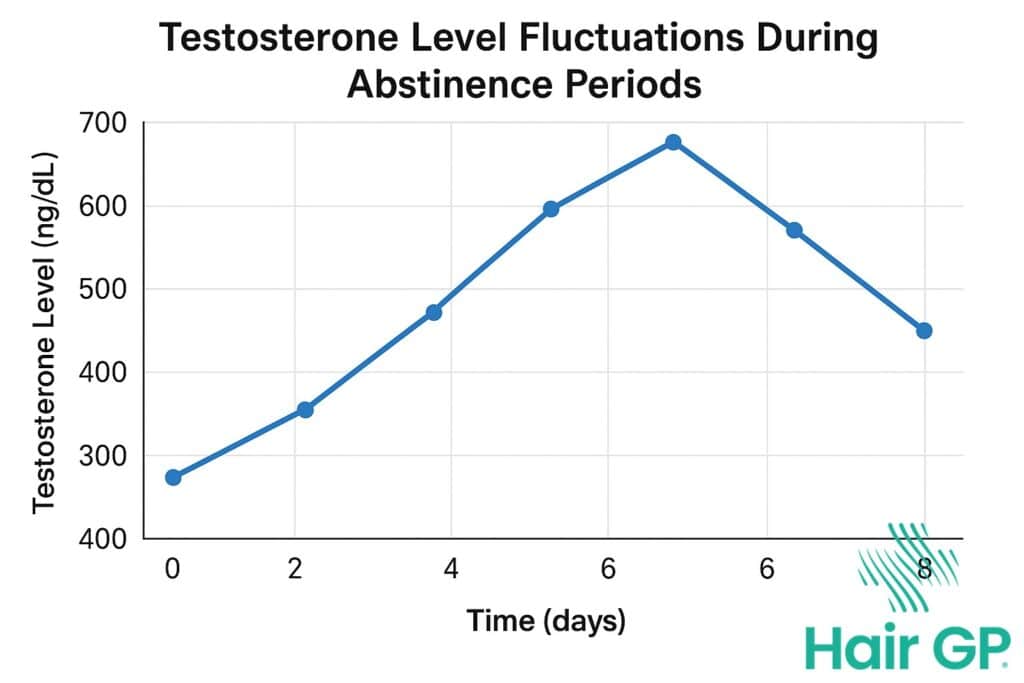
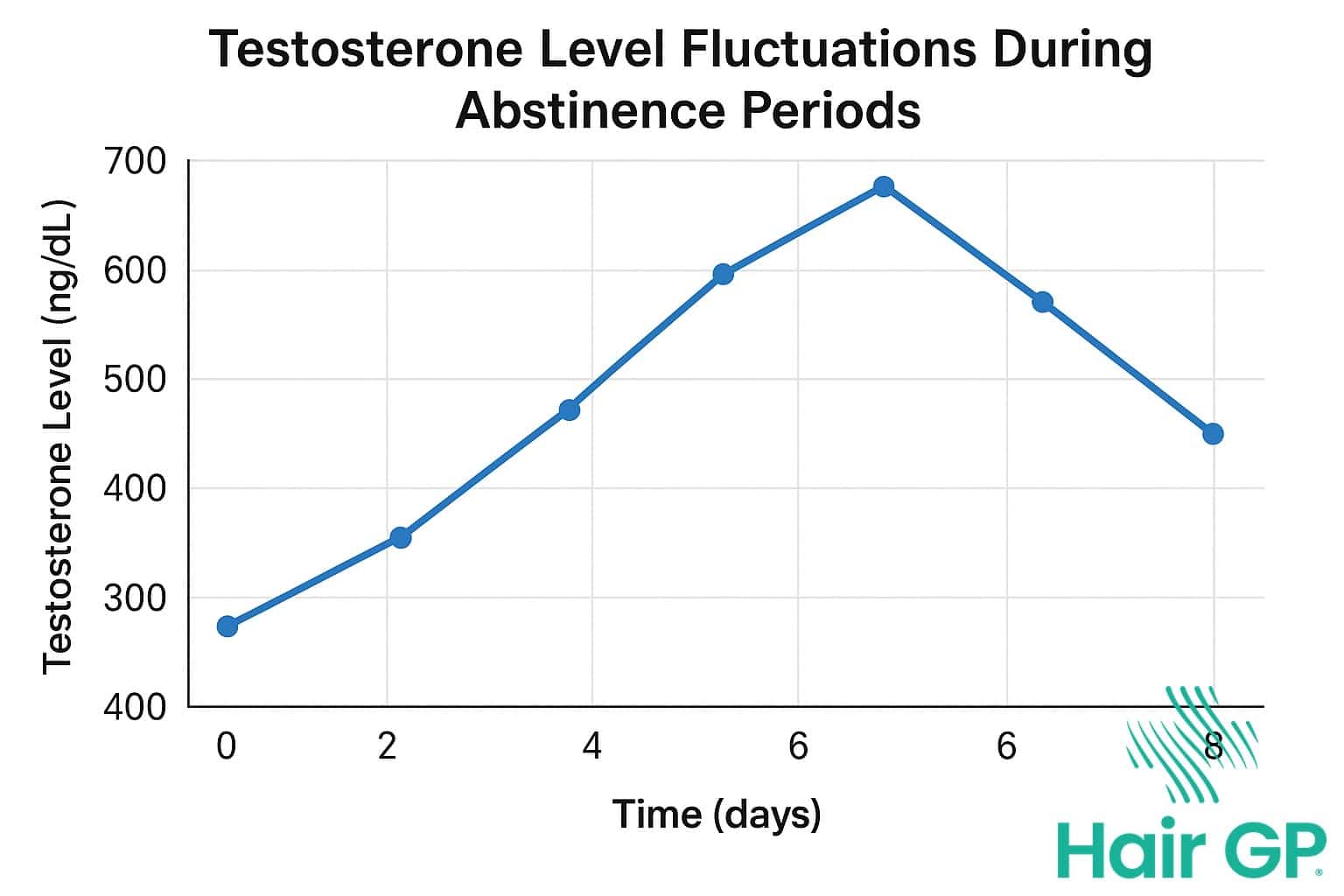
Does Celibacy Increase Testosterone Levels?
Scientific research examining the relationship between sexual abstinence and testosterone production reveals a complex picture that challenges common assumptions. While celibacy does influence hormone levels, the effects are far more nuanced than many popular claims suggest.
Short-Term Testosterone Changes
Studies have documented a notable pattern in testosterone production during brief periods of abstaining. Research demonstrates that testosterone levels remain relatively stable for the first week of abstinence, followed by a significant peak around day seven [3]. This temporary elevation sees testosterone levels rise approximately 45% above baseline, representing the highest point during short-term semen retention periods. However, this peak is remarkably short-lived, with hormone levels returning to normal ranges within days through natural homeostatic regulation. The body’s endocrine system maintains testosterone production within established parameters, preventing sustained elevated testosterone levels from occurring through abstinence alone. This temporary spike likely reflects the body’s natural regulatory mechanisms rather than a sustained benefit of celibacy.
Long-Term Effects on Hormone Production
Extended periods of abstinence reveal different hormonal patterns compared to short-term changes. Long-term studies indicate that testosterone production normalises after the initial peak, with levels typically returning to individual baseline ranges [4]. The body’s homeostatic mechanisms prevent chronically higher testosterone levels from developing through extended celibacy periods. Individual variations in hormone response mean some men may experience slight fluctuations, but sustained elevation above normal ranges remains uncommon. Those with existing low testosterone levels are unlikely to achieve clinically significant improvements through abstinence alone, as underlying hormonal imbalances require medical intervention rather than behavioural modifications.
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness and Hormonal Factors
Male pattern baldness affects the majority of men and results from a complex interplay of genetic predisposition and hormonal factors. While lifestyle choices are often blamed for hair loss, scientific evidence reveals that inherited traits and sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) play the dominant role in determining who experiences alopecia.
Primary Causes of Hair Loss in Men
Genetic predisposition accounts for approximately 80% of male pattern baldness cases, with multiple genes contributing to an individual’s susceptibility to androgenetic alopecia [5]. The primary culprit is sensitivity to DHT, a potent sex hormone derived from testosterone that causes hair follicles to shrink progressively. When DHT binds to receptors in genetically susceptible follicles, it triggers a miniaturisation process that gradually reduces hair shaft diameter and shortens the growth phase.
DHT sensitivity varies significantly between individuals, with studies showing that men with androgenetic alopecia have increased 5α-reductase activity and higher DHT levels in affected scalp areas [6]. Age-related changes compound these genetic factors, as hormone levels fluctuate and follicle sensitivity increases over time. This combination explains why male pattern baldness typically begins in the twenties or thirties and progresses predictably throughout life.
Lifestyle Factors vs Genetic Factors
Research consistently demonstrates that genetic factors vastly outweigh lifestyle influences in determining hair health outcomes. Comparative studies reveal that whilst stress, nutrition, and other environmental factors may influence hair quality, they rarely cause permanent baldness in genetically resistant individuals [7]. Conversely, men with strong genetic predisposition will likely experience significant hair loss regardless of lifestyle modifications.
This evidence-based analysis helps dispel common misconceptions about hair loss prevention through lifestyle changes alone. Whilst maintaining overall health supports optimal hair growth, the fundamental drivers of male pattern baldness remain largely beyond individual control, residing in inherited genetic variations that determine follicle sensitivity to hormonal influences.
Debunking Common Myths About Excessive Masturbation and Hair Loss
Despite widespread internet claims, excessive masturbation does not directly cause hair loss or male pattern baldness. This persistent myth stems from misconceptions about how ejaculation frequency affects hormone levels and hair follicle health. Scientific evidence consistently shows that masturbation, whether frequent or occasional, has no significant impact on testosterone levels that would lead to accelerated hair loss.
Research examining ejaculation frequency and health outcomes demonstrates that frequent ejaculation actually correlates with several health benefits rather than detrimental effects. Studies measuring hormone levels before and after masturbation show only temporary fluctuations that return to baseline within hours, not the sustained changes required to influence hair growth patterns [9].
The confusion often arises from misunderstanding the relationship between DHT and hair loss. While DHT sensitivity does cause male pattern baldness, frequent masturbation does not increase DHT production to levels that would accelerate this process. Hair loss patterns are primarily determined by genetic factors and age-related hormonal changes, not sexual activity frequency.
Medical professionals emphasise that masturbation is a normal aspect of human sexuality with no adverse effects on hair health. Those experiencing hair loss should consult healthcare providers about proven treatments rather than restricting normal sexual behaviours based on unfounded myths. Understanding the science helps separate legitimate concerns from internet misinformation about masturbation and hair loss.
Health Benefits and Risks of Extended Celibacy
Extended celibacy presents a complex array of health benefits and risks that extend far beyond popular misconceptions about testosterone and hair growth. Scientific research reveals both positive and negative health outcomes associated with prolonged periods without sexual activity, requiring careful consideration of individual circumstances and overall wellbeing.
Documented Health Effects
Prostate health considerations represent one of the most studied aspects of celibacy’s impact on men’s health. Research indicates that men with higher ejaculation frequency may experience reduced prostate cancer risk [8], though the relationship remains complex and multifaceted. However, extended celibacy does not directly cause serious health conditions, despite common misconceptions about potential complications.
Psychological effects of celibacy vary significantly among individuals, with some reporting improved mental clarity and reduced anxiety, whilst others experience increased stress or low libido. The physical discomfort sometimes described as ‘blue balls’ or epididymal hypertension typically resolves naturally and poses no long-term health risks. Some men may experience temporary erectile dysfunction related to reduced sexual activity, though this generally improves with resumed sexual function.
Relationship impacts and social connections often influence the overall health benefits or drawbacks of celibacy. The key lies in understanding that celibacy’s effects depend largely on individual circumstances, motivation, and overall lifestyle factors rather than representing universal health outcomes.
Conclusion
The evidence clearly demonstrates that celibacy does not provide significant or lasting benefits for hair growth or testosterone levels. While short-term abstinence may cause temporary fluctuations in testosterone levels, these changes normalise quickly and do not translate into meaningful improvements for male pattern baldness or overall hair health.
Throughout this analysis, we’ve examined the complex relationship between hormonal factors and hair loss, revealing that DHT sensitivity remains the primary driver of male pattern baldness rather than baseline testosterone levels. The temporary spike in testosterone observed during brief periods of celibacy fails to address the underlying genetic and hormonal mechanisms responsible for hair thinning.
For men seeking genuine health benefits and improved hair growth, evidence-based approaches prove far more effective than relying on celibacy. These include consulting healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis, exploring proven treatments like minoxidil or finasteride, maintaining proper nutrition, managing stress levels, and addressing any underlying health conditions.
Rather than pursuing unsubstantiated claims about celibacy’s effects on hair growth, individuals experiencing hair loss should focus on scientifically validated interventions. The relationship between testosterone levels and hair health is far more nuanced than popular misconceptions suggest, making professional medical guidance essential for achieving meaningful results in hair restoration and overall wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, testosterone levels typically peak around day 7 of abstinence then return to baseline. Long-term celibacy doesn’t permanently increase testosterone levels due to natural hormonal regulation.
There’s no scientific evidence that semen retention can reverse or prevent male pattern baldness. Hair loss is primarily driven by genetics and DHT sensitivity, not ejaculation frequency.
Normal masturbation doesn’t negatively affect hair growth. Claims about masturbation causing hair loss lack scientific support and are often based on myths rather than medical evidence.
Proven treatments include FDA-approved medications like finasteride and minoxidil, hair transplant procedures, and lifestyle factors like proper nutrition and stress management.
References
- Adil A, Godwin M. The effectiveness of treatments for androgenetic alopecia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77(1):136-141.e5. PMID: 28396101
- Ho CH, Sood T, Zito PM. Androgenetic Alopecia. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2019. PMID: 31217429
- Jiang M, Xin J, Zou D, Shen JW. A research on the relationship between ejaculation and serum testosterone level in men. J Zhejiang Univ Sci. 2003;4(2):236-40. PMID: 12659241
- Exton MS, Krüger TH, Bursch N, et al. Endocrine response to masturbation-induced orgasm in healthy men following a 3-week sexual abstinence. World J Urol. 2001;19(5):377-82. PMID: 11760788
- Heilmann-Heimbach S, Herold C, Hochfeld LM, et al. Meta-analysis identifies novel risk loci and yields systematic insights into the biology of male-pattern baldness. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):14694. PMID: 28272467
- Kinter KJ, Anekar AA. Biochemistry, Dihydrotestosterone. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2018. PMID: 32491566
- Guo EL, Katta R. Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017;7(1):1-10. PMID: 28243487
- Rider JR, Wilson KM, Sinnott JA, et al. Ejaculation Frequency and Risk of Prostate Cancer: Updated Results with an Additional Decade of Follow-up. Eur Urol. 2016;70(6):974-982. PMID: 27033442
- Isenmann, E., Schumann, M., Notbohm, H. L., Flenker, U., & Zimmer, P. (2021). Hormonal response after masturbation in young healthy men–a randomized controlled cross-over pilot study. Basic and clinical andrology, 31, 1-7. PMID: 33491666